Nox4 NADPH oxidase mediates oxidative stress and apoptosis caused by TNF-alpha in cerebral vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 19118162
- PMCID: PMC2660262
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00381.2008
Nox4 NADPH oxidase mediates oxidative stress and apoptosis caused by TNF-alpha in cerebral vascular endothelial cells
Abstract
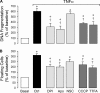
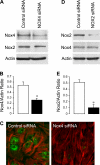
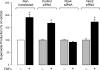
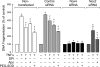
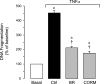
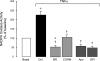
Inflammatory brain disease may damage cerebral vascular endothelium leading to cerebral blood flow dysregulation. The proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (CMVEC) from newborn pigs. We investigated contribution of major cellular sources of reactive oxygen species to endothelial inflammatory response. Nitric oxide synthase and xanthine oxidase inhibitors (N(omega)-nitro-l-arginine and allopurinol) had no effect, while mitochondrial electron transport inhibitors (CCCP, 2-thenoyltrifluoroacetone, and rotenone) attenuated TNF-alpha-induced superoxide (O(2)(*-)) and apoptosis. NADPH oxidase inhibitors (diphenylene iodonium and apocynin) greatly reduced TNF-alpha-evoked O(2)(*-) generation and apoptosis. TNF-alpha rapidly increased NADPH oxidase activity in CMVEC. Nox4, the cell-specific catalytic subunit of NADPH oxidase, is highly expressed in CMVEC, contributes to basal O(2)(*-) production, and accounts for a burst of oxidative stress in response to TNF-alpha. Nox4 small interfering RNA, but not Nox2, knockdown prevented oxidative stress and apoptosis caused by TNF-alpha in CMVEC. Nox4 is colocalized with HO-2, the constitutive isoform of heme oxygenase (HO), which is critical for endothelial protection against TNF-alpha toxicity. The products of HO activity, bilirubin and carbon monoxide (CO, as a CO-releasing molecule, CORM-A1), inhibited Nox4-generated O(2)(*-) and apoptosis caused by TNF-alpha stimulation. We conclude that Nox4 is the primary source of inflammation- and TNF-alpha-induced oxidative stress leading to apoptosis in brain endothelial cells. The ability of CO and bilirubin to combat TNF-alpha-induced oxidative stress by inhibiting Nox4 activity and/or by O(2)(*-) scavenging, taken together with close intracellular compartmentalization of HO-2 and Nox4 in cerebral vascular endothelium, may contribute to HO-2 cytoprotection against inflammatory cerebrovascular disease.
Figures
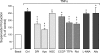




References
-
- Abraham NG, Kappas A. Pharmacological and clinical aspects of heme oxygenase. Pharmacol Rev 60: 79–127, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Ago T, Kitazono T, Ooboshi H, Iyama T, Han YH, Takada J, Wakisaka M, Ibayashi S, Utsumi H, Iida M. Nox4 as the major catalytic component of an endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase. Circulation 109: 227–233, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Barone FC, Arvin B, White RF, Miller A, Webb CL, Willette RN, Lysko PG, Feuerstein GZ. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 28: 1233–1244, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Basuroy S, Bhattacharya S, Tcheranova D, Qu Y, Regan RF, Leffler CW, Parfenova H. HO-2 provides endogenous protection against oxidative stress and apoptosis caused by TNF-α in cerebral vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291: C897–C908, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

