Stimulus-induced changes in blood flow and 2-deoxyglucose uptake dissociate in ipsilateral somatosensory cortex
- PMID: 19118167
- PMCID: PMC2655308
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4307-08.2008
Stimulus-induced changes in blood flow and 2-deoxyglucose uptake dissociate in ipsilateral somatosensory cortex
Abstract
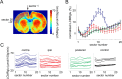
The present study addresses the relationship between blood flow and glucose consumption in rat primary somatosensory cortex (SI) in vivo. We examined bilateral neuronal and hemodynamic changes and 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) uptake, as measured by autoradiography, in response to unilateral forepaw stimulation. In contrast to the contralateral forepaw area, where neuronal activity, blood oxygenation/flow and 2DG uptake increased in unison, we observed, in the ipsilateral SI, a blood oxygenation/flow decrease and arteriolar vasoconstriction in the presence of increased 2DG uptake. Laminar electrophysiological recordings revealed an increase in ipsilateral spiking consistent with the observed increase in 2DG uptake. The vasoconstriction and the decrease in blood flow in the presence of an increase in 2DG uptake in the ipsilateral SI contradict the prominent metabolic hypothesis regarding the regulation of cerebral blood flow, which postulates that the state of neuroglial energy consumption determines the regional blood flow through the production of vasoactive metabolites. We propose that other factors, such as neuronal (and glial) release of messenger molecules, might play a dominant role in the regulation of blood flow in vivo in response to a physiological stimulus.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS-053684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048422/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB003832/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- RR021907/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS053684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB00790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS063226/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS-055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-48422/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB2066/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS-057476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-059832/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
