Sensory responses during sleep in primate primary and secondary auditory cortex
- PMID: 19118181
- PMCID: PMC3844765
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3086-08.2008
Sensory responses during sleep in primate primary and secondary auditory cortex
Abstract
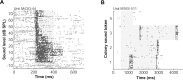
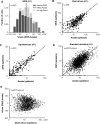
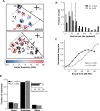
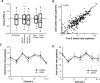
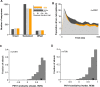
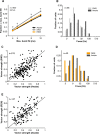
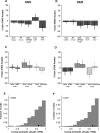
Most sensory stimuli do not reach conscious perception during sleep. It has been thought that the thalamus prevents the relay of sensory information to cortex during sleep, but the consequences for cortical responses to sensory signals in this physiological state remain unclear. We recorded from two auditory cortical areas downstream of the thalamus in naturally sleeping marmoset monkeys. Single neurons in primary auditory cortex either increased or decreased their responses during sleep compared with wakefulness. In lateral belt, a secondary auditory cortical area, the response modulation was also bidirectional and showed no clear systematic depressive effect of sleep. When averaged across neurons, sound-evoked activity in these two auditory cortical areas was surprisingly well preserved during sleep. Neural responses to acoustic stimulation were present during both slow-wave and rapid-eye movement sleep, were repeatedly observed over multiple sleep cycles, and demonstrated similar discharge patterns to the responses recorded during wakefulness in the same neuron. Our results suggest that the thalamus is not as effective a gate for the flow of sensory information as previously thought. At the cortical stage, a novel pattern of activation/deactivation appears across neurons. Because the neural signal reaches as far as secondary auditory cortex, this leaves open the possibility of altered sensory processing of auditory information during sleep.
Figures




References
-
- BarthóP, Hirase H, Monconduit L, Zugaro M, Harris KD, Buzsáki G (2004) Characterization of neocortical principal cells and interneurons by network interactions and extracellular features. J Neurophysiol 92:600–608. - PubMed
-
- BastujiH, Perrin F, Garcia-Larrea L (2002) Semantic analysis of auditory input during sleep: studies with event related potentials. Int J Psychophysiol 46:243–255. - PubMed
-
- BehHC, Barratt PE (1965) Discrimination and conditioning during sleep as indicated by the electroencephalogram. Science 147:1470–1471. - PubMed
-
- BensonDA, Hienz RD (1978) Single-unit activity in the auditory cortex of monkeys selectively attending left vs. right ear stimuli. Brain Res 159:307–320. - PubMed
-
- BonnetMH (1982) Performance during sleep. In: Biological rhythms, sleep and performance (Webb WB, ed), pp 205–237. Chichester, UK: Wiley.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
