The mechanical integrin cycle
- PMID: 19118210
- PMCID: PMC6518156
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.042127
The mechanical integrin cycle
Erratum in
- J Cell Sci. 2009 Feb 15;122(Pt 4):575
Abstract
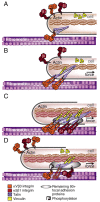
Cells govern tissue shape by exerting highly regulated forces at sites of matrix adhesion. As the major force-bearing adhesion-receptor protein, integrins have a central role in how cells sense and respond to the mechanics of their surroundings. Recent studies have shown that a key aspect of mechanotransduction is the cycle by which integrins bind to the matrix at the leading cell edge, attach to the cytoskeleton, transduce mechanical force, aggregate in the plasma membrane as part of increasingly strengthened adhesion complexes, unbind and, ultimately, are recycled. This mechanical cycle enables the transition from early complexes to larger, more stable adhesions that can then rapidly release. Within this mechanical cycle, integrins themselves exhibit intramolecular conformational change that regulates their binding affinity and may also be dependent upon force. How the cell integrates these dynamic elements into a rigidity response is not clear. Here, we focus on the steps in the integrin mechanical cycle that are sensitive to force and closely linked to integrin function, such as the lateral alignment of integrin aggregates and related adhesion components.
Figures
References
-
- Alexandrova, A. Y., Arnold, K., Schaub, S., Vasiliev, J. M., Meister, J. J., Bershadsky, A. D. and Verkhovsky, A. B. (2008). Comparative dynamics of retrograde actin flow and focal adhesions: formation of nascent adhesions triggers transition from fast to slow flow. PLoS ONE 3, e3234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alon, R. and Dustin, M. L. (2007). Force as a facilitator of integrin conformational changes during leukocyte arrest on blood vessels and antigen-presenting cells. Immunity 26, 17-27. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N. Q., Schwarz, U. S., Riveline, D., Goichberg, P., Tzur, G., Sabanay, I., Mahalu, D., Safran, S., Bershadsky, A., Addadi, L. et al. (2001). Force and focal adhesion assembly: a close relationship studied using elastic micropatterned substrates. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 466-472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

