Integrins in mammary-stem-cell biology and breast-cancer progression--a role in cancer stem cells?
- PMID: 19118213
- PMCID: PMC2714417
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.040394
Integrins in mammary-stem-cell biology and breast-cancer progression--a role in cancer stem cells?
Abstract
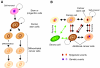
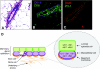
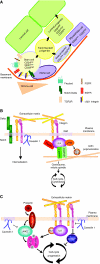
Cancer cells with stem cell-like properties (cancer stem cells) are believed to drive cancer and are associated with poor prognosis. Data from mouse models have demonstrated that integrins, the major cellular receptors for extracellular-matrix components, have essential roles both during cancer initiation and progression, and during cell differentiation in normal development. By presenting an overview of the role of integrins in stem-cell biology and in cancer progression, this Commentary aims to present evidence for a role of integrins in the biology of cancer stem cells. Given the recent interest in the role of integrins in breast-cancer initiation and progression, we focus on the role of the members of the integrin family and their coupled signaling pathways in mammary-gland development and tumorigenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Asselin-Labat, M. L., Shackleton, M., Stingl, J., Vaillant, F., Forrest, N. C., Eaves, C. J., Visvader, J. E., Lindeman, G. J. (2006) Steroid hormone receptor status of mouse mammary stem cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 98, 1011-1014. - PubMed
-
- Asselin-Labat, M. L., Sutherland, K. D., Barker, H., Thomas, R., Shackleton, M., Forrest, N. C., Hartley, L., Robb, L., Grosveld, F. G., van der, W. J. et al. (2007). Gata-3 is an essential regulator of mammary-gland morphogenesis and luminal-cell differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 201-209. - PubMed
-
- Bao, S., Wu, Q., McLendon, R. E., Hao, Y., Shi, Q., Hjelmeland, A. B., Dewhirst, M. W., Bigner, D. D. and Rich, J. N. (2006). Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444, 756-760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

