The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure unravels signalling by receptor clustering
- PMID: 19118384
- PMCID: PMC2661029
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07606
The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure unravels signalling by receptor clustering
Abstract
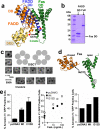
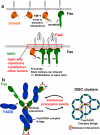
The death inducing signalling complex (DISC) formed by Fas receptor, FADD (Fas-associated death domain protein) and caspase 8 is a pivotal trigger of apoptosis. The Fas-FADD DISC represents a receptor platform, which once assembled initiates the induction of programmed cell death. A highly oligomeric network of homotypic protein interactions comprised of the death domains of Fas and FADD is at the centre of DISC formation. Thus, characterizing the mechanistic basis for the Fas-FADD interaction is crucial for understanding DISC signalling but has remained unclear largely because of a lack of structural data. We have successfully formed and isolated the human Fas-FADD death domain complex and report the 2.7 A crystal structure. The complex shows a tetrameric arrangement of four FADD death domains bound to four Fas death domains. We show that an opening of the Fas death domain exposes the FADD binding site and simultaneously generates a Fas-Fas bridge. The result is a regulatory Fas-FADD complex bridge governed by weak protein-protein interactions revealing a model where the complex itself functions as a mechanistic switch. This switch prevents accidental DISC assembly, yet allows for highly processive DISC formation and clustering upon a sufficient stimulus. In addition to depicting a previously unknown mode of death domain interactions, these results further uncover a mechanism for receptor signalling solely by oligomerization and clustering events.
Figures
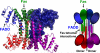

References
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Apoptosis control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:255–60. - PubMed
-
- Peter ME, Krammer PH. The CD95(APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:26–35. - PubMed
-
- Taylor RC, Cullen SP, Martin SJ. Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:231–41. - PubMed
-
- Fesik SW. Insights into programmed cell death through structural biology. Cell. 2000;103:273–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

