Effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor and leukemia inhibiting factor on oxytocin and vasopressin magnocellular neuron survival in rat and mouse hypothalamic organotypic cultures
- PMID: 19118574
- PMCID: PMC2637930
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.12.004
Effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor and leukemia inhibiting factor on oxytocin and vasopressin magnocellular neuron survival in rat and mouse hypothalamic organotypic cultures
Abstract
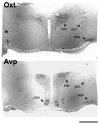
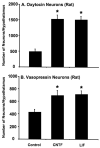
Organotypic cultures of mouse and rat magnocellular neurons (MCNs) in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system (HNS) have served as important experimental models for the molecular and physiological study of this neuronal phenotype. However, it has been difficult to maintain significant numbers of the MCNs, particularly vasopressin MCNs, in these cultures for long periods. In this paper, we describe the use of the neurotrophic factors, leukemia inhibiting factor (LIF) and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) to rescue rat vasopressin (Avp)- and oxytocin (Oxt)-MCNs from axotomy-induced, programmed cell death in vitro. Quantitative data are presented for the efficacy of the LIF family of neurotrophic factors on the survival of MCNs in three nuclei, the paraventricular (PVN), supraoptic (SON), and accessory (ACC) nuclei in the mouse and rat hypothalamus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ciliary neurotrophic factor increases the survival of magnocellular vasopressin and oxytocin neurons in rat supraoptic nucleus in organotypic cultures.Microsc Res Tech. 2002 Jan 15;56(2):101-12. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10015. Microsc Res Tech. 2002. PMID: 11810713
-
Long-term effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor on the survival of vasopressin magnocellular neurones in the rat supraoptic nucleus in vitro.J Neuroendocrinol. 2003 Oct;15(10):933-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2003.01080.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12969237
-
Immunohistochemical analysis of magnocellular elements in rat hypothalamus: distribution and numbers of cells containing neurophysin, oxytocin, and vasopressin.J Comp Neurol. 1981 May 1;198(1):45-64. doi: 10.1002/cne.901980106. J Comp Neurol. 1981. PMID: 7014660
-
Cell-specific gene expression in oxytocin and vasopressin magnocellular neurons.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;449:15-27. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4871-3_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 10026782 Review.
-
Multiple signalling modalities mediated by dendritic exocytosis of oxytocin and vasopressin.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Jul 5;370(1672):20140182. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0182. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26009761 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the Jak-STAT pathway prevents CNTF-mediated survival of axotomized oxytocinergic magnocellular neurons in organotypic cultures of the rat supraoptic nucleus.Exp Neurol. 2013 Feb;240:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.10.023. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Exp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23123407 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of ex Vivo Rodent Platforms in Neuroscience Translational Research With Attention to the 3Rs Philosophy.Front Vet Sci. 2018 Jul 19;5:164. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00164. eCollection 2018. Front Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 30073174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal activity and axonal sprouting differentially regulate CNTF and CNTF receptor complex in the rat supraoptic nucleus.Exp Neurol. 2012 Jan;233(1):243-52. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.10.009. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22037350 Free PMC article.
-
The MAPK and PI3K pathways mediate CNTF-induced neuronal survival and process outgrowth in hypothalamic organotypic cultures.J Cell Commun Signal. 2015 Sep;9(3):217-31. doi: 10.1007/s12079-015-0268-8. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 25698661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso G, Bribes E, Chauvet N. Survival and regeneration of neurons of the supraoptic nucleus following surgical transection of neurohypophysial axons depend on the existence of collateral projections of these neurons to the dorsolateral hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1996;711:34–43. - PubMed
-
- Arima H, House SB, Gainer H, Aguilera G. Direct stimulation of arginine vasopressin gene transcription by cAMP in parvocellular neurons of the paraventricular nucleus in organotypic cultures. Endocrinology. 2001;142:5027–30. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong WE, Warach S, Hatton GI, McNeill TH. Subnuclei in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: a cytoarchitectural, horseradish peroxidase and immunocytochemical analysis. Neuroscience. 1980;5:1931–58. - PubMed
-
- Bali B, Ferenczi S, Kovacs KJ. Direct inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on corticotrophin-releasing hormone gene expression in neurones of the paraventricular nucleus in rat hypothalamic organotypic cultures. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008;20:1045–51. - PubMed
-
- Baratta J, Marienhagen JW, Ha D, Yu J, Robertson RT. Cholinergic innervation of cerebral cortex in organotypic slice cultures: sustained basal forebrain and transient striatal cholinergic projections. Neuroscience. 1996;72:1117–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

