Genome-wide association study implicates a chromosome 12 risk locus for late-onset Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 19118814
- PMCID: PMC2668056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.12.008
Genome-wide association study implicates a chromosome 12 risk locus for late-onset Alzheimer disease
Abstract
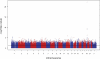
Only Apolipoprotein E polymorphisms have been consistently associated with the risk of late-onset Alzheimer disease (LOAD), but they represent only a minority of the underlying genetic effect. To identify additional LOAD risk loci, we performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) on 492 LOAD cases and 498 cognitive controls using Illumina's HumanHap550 beadchip. An additional 238 cases and 220 controls were used as a validation data set for single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that met genome-wide significance. To validate additional associated SNPs (p < 0.0001) and nominally associated candidate genes, we imputed SNPs from our GWAS using a previously published LOAD GWAS(1) and the IMPUTE program. Association testing was performed with the Cochran-Armitage trend test and logistic regression, and genome-wide significance was determined with the False Discovery Rate-Beta Uniform Mixture method. Extensive quality-control methods were performed at both the sample and the SNP level. The GWAS confirmed the known APOE association and identified association with a 12q13 locus at genome-wide significance; the 12q13 locus was confirmed in our validation data set. Four additional highly associated signals (1q42, 4q28, 6q14, 19q13) were replicated with the use of the imputed data set, and six candidate genes had SNPs with nominal association in both the GWAS and the joint imputated data set. These results help to further define the genetic architecture of LOAD.
Figures
References
-
- Saunders A.M., Strittmatter W.J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P.H., Pericak-Vance M.A., Joo S.H., Rosi B.L., Gusella J.F., Crapper-MacLachlan D.R., Alberts M.J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
-
- Strittmatter W.J., Saunders A.M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G.S., Roses A.D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1993;90:1977–1981. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corder E.H., Saunders A.M., Strittmatter W.J., Schmechel D.E., Gaskell P.C., Small G.W., Roses A.D., Haines J.L., Pericak-Vance M.A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;512:921–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous