Infection-triggered familial or recurrent cases of acute necrotizing encephalopathy caused by mutations in a component of the nuclear pore, RANBP2
- PMID: 19118815
- PMCID: PMC2668029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.12.009
Infection-triggered familial or recurrent cases of acute necrotizing encephalopathy caused by mutations in a component of the nuclear pore, RANBP2
Abstract
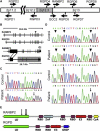
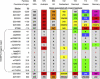
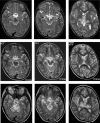
Acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE) is a rapidly progressive encephalopathy that can occur in otherwise healthy children after common viral infections such as influenza and parainfluenza. Most ANE is sporadic and nonrecurrent (isolated ANE). However, we identified a 7 Mb interval containing a susceptibility locus (ANE1) in a family segregating recurrent ANE as an incompletely penetrant, autosomal-dominant trait. We now report that all affected individuals and obligate carriers in this family are heterozygous for a missense mutation (c.1880C-->T, p.Thr585Met) in the gene encoding the nuclear pore protein Ran Binding Protein 2 (RANBP2). To determine whether this mutation is the susceptibility allele, we screened controls and other patients with ANE who are unrelated to the index family. Patients from 9 of 15 additional kindreds with familial or recurrent ANE had the identical mutation. It arose de novo in two families and independently in several other families. Two other patients with familial ANE had different RANBP2 missense mutations that altered conserved residues. None of the three RANBP2 missense mutations were found in 19 patients with isolated ANE or in unaffected controls. We conclude that missense mutations in RANBP2 are susceptibility alleles for familial and recurrent cases of ANE.
Figures

References
-
- Liu R., Paxton W.A., Choe S., Ceradini D., Martin S.R., Horuk R., MacDonald M.E., Stuhlmann H., Koup R.A., Landau N.R. Homozygous defect in HIV-1 coreceptor accounts for resistance of some multiply-exposed individuals to HIV-1 infection. Cell. 1996;86:367–377. - PubMed
-
- Mori S.I., Nagashima M., Sasaki Y., Mori K., Tabei Y., Yoshida Y., Yamazaki K., Hirata I., Sekine H., Ito T. A novel amino acid substitution at the receptor-binding site on the hemagglutinin of H3N2 influenza A viruses isolated from 6 cases with acute encephalopathy during the 1997–1998 season in Tokyo. Arch. Virol. 1999;144:147–155. - PubMed
-
- Mizuguchi M. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood: a novel form of acute encephalopathy prevalent in Japan and Taiwan. Brain Dev. 1997;19:81–92. - PubMed
-
- Mizuguchi M., Yamanouchi H., Ichiyama T., Shiomi M. Acute encephalopathy associated with influenza and other viral infections. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2007;115:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Mastroyianni S.D., Gionnis D., Voudris K., Skardoutsou A., Mizuguchi M. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy of childhood in non-Asian patients: report of three cases and literature review. J. Child Neurol. 2006;21:872–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

