Three distinct condensin complexes control C. elegans chromosome dynamics
- PMID: 19119011
- PMCID: PMC2682549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.12.006
Three distinct condensin complexes control C. elegans chromosome dynamics
Erratum in
- Curr Biol. 2009 Jan 27;19(2):176. Sarkesik, Ali [corrected to Sarkeshik, Ali]
Abstract
Background: Condensin complexes organize chromosome structure and facilitate chromosome segregation. Higher eukaryotes have two complexes, condensin I and condensin II, each essential for chromosome segregation. The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans was considered an exception, because it has a mitotic condensin II complex but appeared to lack mitotic condensin I. Instead, its condensin I-like complex (here called condensin I(DC)) dampens gene expression along hermaphrodite X chromosomes during dosage compensation.
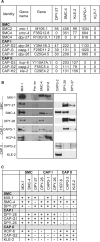
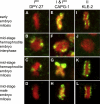
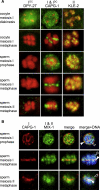
Results: Here we report the discovery of a third condensin complex, condensin I, in C. elegans. We identify new condensin subunits and show that each complex has a conserved five-subunit composition. Condensin I differs from condensin I(DC) by only a single subunit. Yet condensin I binds to autosomes and X chromosomes in both sexes to promote chromosome segregation, whereas condensin I(DC) binds specifically to X chromosomes in hermaphrodites to regulate transcript levels. Both condensin I and II promote chromosome segregation, but associate with different chromosomal regions during mitosis and meiosis. Unexpectedly, condensin I also localizes to regions of cohesion between meiotic chromosomes before their segregation.
Conclusions: We demonstrate that condensin subunits in C. elegans form three complexes, one that functions in dosage compensation and two that function in mitosis and meiosis. These results highlight how the duplication and divergence of condensin subunits during evolution may facilitate their adaptation to specialized chromosomal roles and illustrate the versatility of condensins to function in both gene regulation and chromosome segregation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Condensin function in dosage compensation.Epigenetics. 2009 May 16;4(4):212-5. doi: 10.4161/epi.8957. Epub 2009 May 7. Epigenetics. 2009. PMID: 19483464 Review.
-
Chromosome dynamics: the case of the missing condensin.Curr Biol. 2009 Feb 10;19(3):R127-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.12.004. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19211053 Review.
-
An SMC-like protein binds and regulates Caenorhabditis elegans condensins.PLoS Genet. 2017 Mar 16;13(3):e1006614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006614. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28301465 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans dosage compensation: a window into mechanisms of domain-scale gene regulation.Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):215-27. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-9011-0. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308702 Review.
-
C. elegans condensin promotes mitotic chromosome architecture, centromere organization, and sister chromatid segregation during mitosis and meiosis.Genes Dev. 2002 Mar 15;16(6):729-42. doi: 10.1101/gad.968302. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11914278 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
XOL-1 regulates developmental timing by modulating the H3K9 landscape in C. elegans early embryos.PLoS Genet. 2024 Aug 15;20(8):e1011238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011238. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39146391 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights Into the Mechanism by Which 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Improves Thermotolerance in Lentinula edodes.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 20;13:910255. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.910255. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35801117 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of an X-Specific Condensin Correlates with a Reduction in Active Histone Modifications at Gene Regulatory Elements.Genetics. 2019 Jul;212(3):729-742. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302254. Epub 2019 May 22. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31123040 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic identification of germline proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans.Worm. 2015 Feb 9;4(1):e1008903. doi: 10.1080/21624054.2015.1008903. eCollection 2015 Jan-Mar. Worm. 2015. PMID: 26435885 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent action of the RNA binding protein FOX-1 to relay X-chromosome number and determine C. elegans sex.Elife. 2020 Dec 29;9:e62963. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62963. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33372658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belmont AS. Mitotic chromosome structure and condensation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006;18:632–638. - PubMed
-
- Hirano T. Condensins: organizing and segregating the genome. Curr. Biol. 2005;15:R265–R275. - PubMed
-
- Hirota T, Gerlich D, Koch B, Ellenberg J, Peters JM. Distinct functions of condensin I and II in mitotic chromosome assembly. J. Cell Sci. 2004;117:6435–6445. - PubMed
-
- Ono T, Losada A, Hirano M, Myers MP, Neuwald AF, Hirano T. Differential contributions of condensin I and condensin II to mitotic chromosome architecture in vertebrate cells. Cell. 2003;115:109–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

