A DNA polymerase-{alpha}{middle dot}primase cofactor with homology to replication protein A-32 regulates DNA replication in mammalian cells
- PMID: 19119139
- PMCID: PMC2645831
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M807593200
A DNA polymerase-{alpha}{middle dot}primase cofactor with homology to replication protein A-32 regulates DNA replication in mammalian cells
Abstract
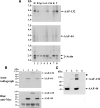
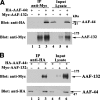
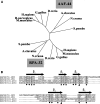
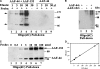
alpha-Accessory factor (AAF) stimulates the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha.primase, the only enzyme known to initiate DNA replication in eukaryotic cells ( Goulian, M., Heard, C. J., and Grimm, S. L. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 13221-13230 ). We purified the AAF heterodimer composed of 44- and 132-kDa subunits from cultured cells and identified full-length cDNA clones using amino acid sequences from internal peptides. AAF-132 demonstrated no homologies to known proteins; AAF-44, however, is evolutionarily related to the 32-kDa subunit of replication protein A (RPA-32) and contains an oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold domain similar to the OB fold domains of RPA involved in single-stranded DNA binding. Epitope-tagged versions of AAF-44 and -132 formed a complex in intact cells, and purified recombinant AAF-44 bound to single-stranded DNA and stimulated DNA primase activity only in the presence of AAF-132. Mutations in conserved residues within the OB fold of AAF-44 reduced DNA binding activity of the AAF-44.AAF-132 complex. Immunofluorescence staining of AAF-44 and AAF-132 in S phase-enriched HeLa cells demonstrated punctate nuclear staining, and AAF co-localized with proliferating cell nuclear antigen, a marker for replication foci containing DNA polymerase-alpha.primase and RPA. Small interfering RNA-mediated depletion of AAF-44 in tumor cell lines inhibited [methyl-(3)H]thymidine uptake into DNA but did not affect cell viability. We conclude that AAF shares structural and functional similarities with RPA-32 and regulates DNA replication, consistent with its ability to increase polymerase-alpha.primase template affinity and stimulate both DNA primase and polymerase-alpha activities in vitro.
Figures



References
-
- Bell, S. P., and Dutta, A. (2002) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71333 -374 - PubMed
-
- Garg, P., and Burgers, P. M. (2005) Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40115 -128 - PubMed
-
- Bochkareva, E., Frappier, L., Edwards, A. M., and Bochkarev, A. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 2733932 -3936 - PubMed
-
- Frick, D. N., and Richardson, C. C. (2001) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 7039 -80 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

