FTY720 inhibits ceramide synthases and up-regulates dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate formation in human lung endothelial cells
- PMID: 19119142
- PMCID: PMC2645812
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805186200
FTY720 inhibits ceramide synthases and up-regulates dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate formation in human lung endothelial cells
Abstract
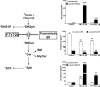
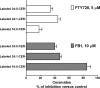
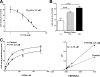
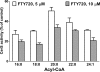
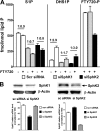
Novel immunomodulatory molecule FTY720 is a synthetic analog of myriocin, but unlike myriocin FTY720 does not inhibit serine palmitoyltransferase. Although many of the effects of FTY720 are ascribed to its phosphorylation and subsequent sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)-like action through S1P(1,3-5) receptors, studies on modulation of intracellular balance of signaling sphingolipids by FTY720 are limited. In this study, we used stable isotope pulse labeling of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells with l-[U-(13)C, (15)N]serine as well as in vitro enzymatic assays and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry methodology to characterize FTY720 interference with sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis. In human pulmonary artery endothelial cells, FTY720 inhibited ceramide synthases, resulting in decreased cellular levels of dihydroceramides, ceramides, sphingosine, and S1P but increased levels of dihydrosphingosine and dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate (DHS1P). The FTY720-induced modulation of sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis was similar to that of fumonisin B1, a classical inhibitor of ceramide synthases, but differed in the efficiency to inhibit biosynthesis of short-chain versus long-chain ceramides. In vitro kinetic studies revealed that FTY720 is a competitive inhibitor of ceramide synthase 2 toward dihydrosphingosine with an apparent K(i) of 2.15 microm. FTY720-induced up-regulation of DHS1P level was mediated by sphingosine kinase (SphK) 1, but not SphK2, as confirmed by experiments using SphK1/2 silencing with small interfering RNA. Our data demonstrate for the first time the ability of FTY720 to inhibit ceramide synthases and modulate the intracellular balance of signaling sphingolipids. These findings open a novel direction for therapeutic applications of FTY720 that focuses on inhibition of ceramide biosynthesis, ceramide-dependent signaling, and the up-regulation of DHS1P generation in cells.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang, Z., and Schluesener, H. J. (2007) Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 7 845–850 - PubMed
-
- Hiestand, P. C., Rausch, M., Meier, D. P., and Foster, C. A. (2008) Prog. Drug Res. 66 363–381 - PubMed
-
- Mansoor, M., and Melendez, A. J. (2008) Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 3 62–69 - PubMed
-
- Schwab, S. R., and Cyster, J. G. (2007) Nat. Immunol. 8 1295–1301 - PubMed
-
- Lee, M. J., Thangada, S., Claffey, K. P., Ancellin, N., Liu, C. H., Kluk, M., Volpi, M., Sha'afi, R. I., and Hla, T. (1999) Cell 99 301–312 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

