Relationship between serum brain natriuretic peptide and heart function in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 19119256
- PMCID: PMC2687684
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2008.23.4.191
Relationship between serum brain natriuretic peptide and heart function in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background/aims: Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels are known to be elevated in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and normal heart function. Therefore, the present study was performed to examine the effectiveness of BNP level in diagnosing heart failure in patients with CKD and to determine its effects on survival rate and prognosis.
Methods: A total of 182 patients with CKD who visited the hospital due to dyspnea of NYHA class II were included in the study. BNP levels were measured and echocardiography was performed to divide the subjects into groups with and without heart failure. Their BNP levels, clinical courses, and survival rates were analyzed retrospectively.
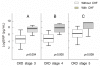
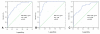
Results: When BNP level was >/=858.5 pg/mL in CKD patients, heart failure could be diagnosed with sensitivity and specificity of 77% and 72%, respectively. Survival rate of the group with BNP levels of >/=858.8 pg/mL was significantly lower than that of the group with BNP level below this threshold (p=0.012) and multivariate analysis showed that BNP level, age, and sex affected survival rate in the group with BNP level >/=858.8 pg/mL.
Conclusions: BNP levels of patients with CKD showed a positive correlation with creatinine levels, and the critical point of BNP level for diagnosis of heart failure was 858.5 pg/mL. As the survival rate in patients with BNP level above the critical point was significantly low, this level was a useful indicator for predicting their prognosis. Care should be taken in interpreting BNP level because patients with stage 5 CKD may show a high concentration of BNP without heart failure.
Figures


References
-
- United States Renal Data System. Causes of death. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;30(2 Suppl):S107–S117. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Herrmann HC, Steg PG, Duc P, Westheim A, Omland T, Knudsen CW, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Lamba S, Wu AH, Perez A, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Maisel AS. B-type natriuretic peptide and clinical judgment in emergency diagnosis of heart failure: analysis from Breathing Not Properly (BNP) Multinational Study. Circulation. 2002;106:416–422. - PubMed
-
- Morrison LK, Harrison A, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Clopton P, Maisel A. Utility of a rapid B-natriuretic peptide assay in differentiating congestive heart failure from lung disease in patients presenting with dyspnea. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:202–209. - PubMed
-
- Mark PB, Stewart GA, Gansevoort RT, Petrie CJ, McDonagh TA, Dargie HJ, Rodger RS, Jardine AG. Diagnostic potential of circulating natriuretic peptides in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:402–410. - PubMed
-
- Takami Y, Horio T, Iwashima Y, Takiuchi S, Kamide K, Yoshihara F, Nakamura S, Nakahama H, Inenaga T, Kangawa K, Kawano Y. Diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma brain natriuretic peptide in non-dialysis-dependent CRF. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:420–428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
