Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antimalarial and antitumor activity of new ruthenium(II) complexes of chloroquine
- PMID: 19119867
- PMCID: PMC2673146
- DOI: 10.1021/ic802220w
Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antimalarial and antitumor activity of new ruthenium(II) complexes of chloroquine
Abstract
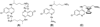
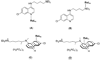
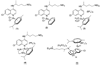
The new Ru(II) chloroquine complexes [Ru(eta(6)-arene)(CQ)Cl2] (CQ = chloroquine; arene = p-cymene 1, benzene 2), [Ru(eta(6)-p-cymene)(CQ)(H2O)2][BF4]2 (3), [Ru(eta(6)-p-cymene)(CQ)(en)][PF6]2 (en = ethylenediamine) (4), and [Ru(eta(6)-p-cymene)(eta(6)-CQDP)][BF4]2 (5, CQDP = chloroquine diphosphate) have been synthesized and characterized by use of a combination of NMR and FTIR spectroscopy with DFT calculations. Each complex is formed as a single coordination isomer: In 1-4, chloroquine binds to ruthenium in the eta(1)-N mode through the quinoline nitrogen atom, whereas in 5 an unprecedented eta(6) bonding through the carbocyclic ring is observed. 1, 2, 3, and 5 are active against CQ-resistant (Dd2, K1, and W2) and CQ-sensitive (FcB1, PFB, F32, and 3D7) malaria parasites (Plasmodium falciparum); importantly, the potency of these complexes against resistant parasites is consistently higher than that of the standard drug chloroquine diphosphate. 1 and 5 also inhibit the growth of colon cancer cells, independently of the p53 status and of liposarcoma tumor cell lines with the latter showing increased sensitivity, especially to 1 (IC50 8 microM); this is significant because this type of tumor does not respond to currently employed chemotherapies.
Figures


References
-
- Sigel A, Sigel H, editors. Metal Ions and Their Complexes in Medication, In Metal Ions in Biological Systems. Vol. 41. New York: Marcel Dekker; 2004.
- Sigel A, Sigel H, editors. Metal complexes in tumor diagnosis and as anticancer agents, In Metal Ions in Biological Systems. Vol. 42 2004.
-
- Jakupec MA, Galanski M, Arion VB, Hartinger CG, Keppler BK. Dalton Trans. 2008:183–194. - PubMed
- Bruijnincx PCA, Sadler PJ. Curr. Op. Chem. Biol. 2008;12:197–206. - PMC - PubMed
- Ronconi L, Sadler PJ. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007;251:1633–1648. - PMC - PubMed
- Dyson PJ, Sava G. Dalton Trans. 2006:1929–1933. - PubMed
- Allardyce CS, Dorcier A, Scolaro C, Dyson PJ. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2005;19:1–10.
- Paschke R, Paetz C, Mueller T, Schmoll H-J, Mueller H, Sorkau E, Sinn E. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003;10:2033–2044. - PubMed
- Galanski M, Arion VB, Jakupec MA, Keppler BK. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003;9:2078–2089. - PubMed
- Zhang CX, Lippard SJ. Curr. Op. Chem. Biol. 2003;7:481–489. - PubMed
- Reedijk J. PNAS. 2003;100:3611–3616. - PMC - PubMed
- McKeage MJ, Maharaj L, Berners-Price SJ. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002;232:127–135.
-
- Sánchez-Delgado RA, Anzellotti A, Suárez L. Metal Ions and their Complexes in Medication. In: Sigel H, Sigel A, editors. Metal Ions in Biological Systems. Vol. 41. New York: Marcel Dekker; 2004.
- Sánchez-Delgado RA, Anzellotti A. Minirev. Med. Chem. 2004;4:23–30. - PubMed
-
- Clarke MJ. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003;236:209–233.
-
- Bratsos I, Jedner S, Gianferrara T, Alessio E. CHIMIA. 2007;61:692–697.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

