Innate immunity to virus infection
- PMID: 19120477
- PMCID: PMC5489343
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00737.x
Innate immunity to virus infection
Abstract
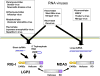
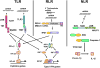
The innate immune system is essential for the initial detection of invading viruses and subsequent activation of adaptive immunity. Three classes of receptors, designated retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs), Toll-like receptors (TLRs), and nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors (NLRs), sense viral components, such as double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), single-stranded RNA, and DNA. RLRs and TLRs play essential roles in the production of type I interferons (IFNs) and proinflammatory cytokines in cell type-specific manners. While the RLRs play essential roles in the recognition of RNA viruses in various cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells utilize TLRs for detecting virus invasion. NLRs play a role in the production of mature interleukin-1 beta to dsRNA stimulation. Activation of innate immune cells is critical for mounting adaptive immune responses. In this review, we discuss recent advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of viral RNA recognition by these different types of receptors and its relation to acquired immune responses.
Figures
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, et al. Genetic analysis of resistance to viral infection. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:753–66. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature. 2007;449:819–26. - PubMed
-
- Petrilli V, Dostert C, Muruve DA, Tschopp J. The inflammasome: a danger sensing complex triggering innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:615–22. - PubMed
-
- Kanneganti TD, Lamkanfi M, Nunez G. Intracellular NOD-like receptors in host defense and disease. Immunity. 2007;27:549–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

