Antagomir-mediated silencing of endothelial cell specific microRNA-126 impairs ischemia-induced angiogenesis
- PMID: 19120690
- PMCID: PMC3828868
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00613.x
Antagomir-mediated silencing of endothelial cell specific microRNA-126 impairs ischemia-induced angiogenesis
Abstract
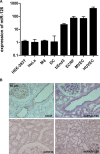
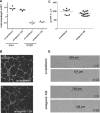
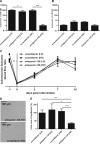
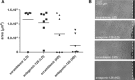
MicroRNAs are negative regulators of gene expression that play a key role in cell-type specific differentiation and modulation of cell function and have been proposed to be involved in neovascularization. Previously, using an extensive cloning and sequencing approach, we identified miR-126 to be specifically and highly expressed in human endothelial cells (EC). Here, we demonstrate EC-specific expression of miR-126 in capillaries and the larger vessels in vivo. We therefore explored the potential role of miR-126 in arteriogenesis and angiogenesis. Using miR-reporter constructs, we show that miR-126 is functionally active in EC in vitro and that it could be specifically repressed using antagomirs specifically targeting miR-126. To study the consequences of miR-126 silencing on vascular regeneration, mice were injected with a single dose of antagomir-126 or a control 'scramblemir' and exposed to ischemia of the left hindlimb by ligation of the femoral artery. Although miR-126 was effectively silenced in mice treated with a single, high dose (HD) of antagomir-126, laser Doppler perfusion imaging did not show effects on blood flow recovery. In contrast, quantification of the capillary density in the gastrocnemius muscle revealed that mice treated with a HD of antagomir-126 had a markedly reduced angiogenic response. Aortic explant cultures of the mice confirmed the role of miR-126 in angiogenesis. Our data demonstrate a facilitary function for miR-126 in ischemia-induced angiogenesis and show the efficacy and specificity of antagomir-induced silencing of EC-specific microRNAs in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–78. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–14. - PubMed
-
- Urbich C, Kuehbacher A, Dimmeler S. Role of microRNAs in vascular diseases, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79:581–8. - PubMed
-
- Kuehbacher A, Urbich C, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Role of Dicer and Drosha for endothelial microRNA expression and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2007;101:59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

