miRNA regulation of cytokine genes
- PMID: 19121586
- PMCID: PMC3129852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.11.010
miRNA regulation of cytokine genes
Abstract
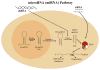
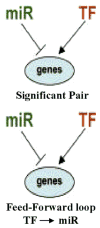
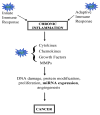
In this review we discuss specific examples of regulation of cytokine genes and focus on a new mechanism involving post-transcriptional regulation via miRNAs. The post-transcriptional regulation of cytokine genes via the destabilizing activity of AU-rich elements [AREs] and miRNAs is a pre-requisite for regulating the half-life of many cytokines and achieving the temporal and spatial distributions required for regulation of these genes.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

