Long-term trends in carpal tunnel syndrome
- PMID: 19122028
- PMCID: PMC2633642
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000338533.88960.b9
Long-term trends in carpal tunnel syndrome
Abstract
Objective: To assess temporal trends in carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) incidence, surgical treatment, and work-related lost time.
Methods: Incident CTS and first-time carpal tunnel release among Olmsted County, Minnesota, residents were identified using the medical records linkage system of the Rochester Epidemiology Project; 80% of a sample were confirmed by medical record review. Work-related CTS was identified from the Minnesota Department of Labor and Industry.
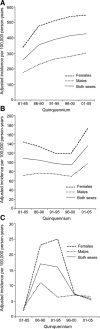
Results: Altogether, 10,069 Olmsted County residents were initially diagnosed with CTS in 1981-2005. Overall incidence (adjusted to the 2000 US population) was 491 and 258 per 100,000 person-years for women vs men (p < 0.0001) and 376 per 100,000 for both sexes combined. Adjusted annual rates increased from 258 per 100,000 in 1981-1985 to 424 in 2000-2005 (p < 0.0001). The average annual incidence of carpal tunnel release surgery was 109 per 100,000, while that for work-related CTS was 11 per 100,000. An increase in young, working-age individuals seeking medical attention for symptoms of less severe CTS in the early to mid-1980s was followed in the 1990s by an increasing incidence in elderly people.
Conclusions: The incidence of medically diagnosed carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) accelerated in the 1980s. The cause of the increase is unclear, but it corresponds to an epidemic of CTS cases resulting in lost work days that began in the mid-1980s and lasted through the mid-1990s. The elderly present with more severe disease and are more likely to have carpal tunnel surgery, which may have significant health policy implications given the aging population.
Figures
References
-
- Palmer DH, Hanrahan LP. Social and economic costs of carpal tunnel surgery. Instr Course Lect 1995;44:167–172. - PubMed
-
- Manktelow RT, Binhammer P, Tomat LR, Bril V, Szalai JP. Carpal tunnel syndrome: cross-sectional and outcome study in Ontario workers. J Hand Surg 2004;29A:307–317. - PubMed
-
- Daniell WE, Fulton-Kehoe D, Chiou LA, Franklin GM. Work-related carpal tunnel syndrome in Washington state workers’ compensation: temporal trends, clinical practices, and disability. Am J Ind Med 2005;48:259–269. - PubMed
-
- Foley M, Silverstein B, Polissar N. The economic burden of carpal tunnel syndrome: long-term earnings of CTS claimants in Washington State. Am J Ind Med 2007;50:155–172. - PubMed
-
- Stevens JC, Sun S, Beard CM, O’Fallon WM, Kurland LT. Carpal tunnel syndrome in Rochester, Minnesota, 1961 to 1980 Neurology 1988;38:134–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
