Incomplete reconstitution of T cell subsets on combination antiretroviral therapy in the AIDS Clinical Trials Group protocol 384
- PMID: 19123865
- PMCID: PMC2676920
- DOI: 10.1086/595888
Incomplete reconstitution of T cell subsets on combination antiretroviral therapy in the AIDS Clinical Trials Group protocol 384
Abstract
Background: Initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) results in higher total CD4 cell counts, a surrogate for immune reconstitution. Whether the baseline CD4 cell count affects reconstitution of immune cell subsets has not been well characterized.
Methods: Using data from 978 patients (621 with comprehensive immunological assessments) from the AIDS [Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome] Clinical Trials Group protocol 384, a randomized trial of initial ART, we compared reconstitution of CD4(+), CD4(+) naive and memory, CD4(+) activation, CD8(+), CD8(+) activation, B, and natural killer cells among patients in different baseline CD4(+) strata. Reference ranges for T cell populations in control patients negative for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection were calculated using data from AIDS Clinical Trials Group protocol A5113.
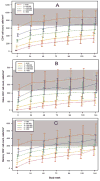
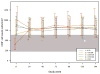
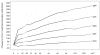
Results: Patients in the lower baseline CD4(+) strata did not achieve total CD4(+) cell counts similar to those of patients in the higher strata during 144 weeks of ART, although CD4(+) cell count increases were similar. Ratios of CD4(+) naive-memory cell counts and CD4(+):CD8(+) cell counts remained significantly reduced in patients with lower baseline CD4(+) cell counts (<or=350 cells/mm(3)). These immune imbalances were most notable for those initiating ART with a baseline CD4(+) cell count <or=200 cells/mm(3), even after adjustment for baseline plasma HIV RNA levels.
Conclusions: After nearly 3 years of ART, T cell subsets in patients with baseline CD4(+) cell counts >350 cells/mm(3) achieved or approached the reference range those of control individuals without HIV infection. In contrast, patients who began ART with <or=350 CD4(+) cells/mm(3) generally did not regain normal CD4(+) naive-memory cell ratios. These results support current guidelines to start ART at a threshold of 350 cells/mm(3) and suggest that there may be immunological benefits associated with initiating therapy at even higher CD4(+) cell counts.
Figures


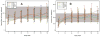


Comment in
-
CD4+ T cell recovery with antiretroviral therapy: more than the sum of the parts.Clin Infect Dis. 2009 Feb 1;48(3):362-4. doi: 10.1086/595889. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19123869 No abstract available.
References
-
- Euroguidelines Group. European guidelines for the clinical management and treatment of HIV infected adults in Europe. European AIDS Clinical Society; 2007. - PubMed
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1–infected adults and adolescents–December 1, 2007. [Accessed 7 January 2008]. Available at: http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/
-
- Lederman MM, McKinnis R, Kelleher D, et al. Cellular restoration in HIV infected persons treated with abacavir and a protease inhibitor: age inversely predicts naive CD4 cell count increase. AIDS. 2000;14:2635–42. - PubMed
-
- Hogg RS, Yip B, Chan KJ, et al. Rates of disease progression by baseline CD4 cell count and viral load after initiating triple-drug therapy. JAMA. 2001;286:2568–77. - PubMed
-
- Opravil M, Ledergerber B, Furrer H, et al. Clinical efficacy of early initiation of HAART in patients with asymptomatic HIV infection and CD4 cell count >350 × 106/l. AIDS. 2002;16:1371–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AI25879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI066992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI066992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01AI062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027666/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27659/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI38855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- IP30AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27666/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI38858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027659/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

