Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and serovar [4,5,12:i:-]
- PMID: 19124586
- PMCID: PMC2648174
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01597-08
Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and serovar [4,5,12:i:-]
Abstract
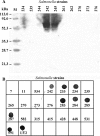
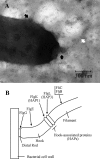
Flagellar extracts of Salmonella enterica serovars expressing phase 2 H1 antigenic complex (H:1,2, H:1,5, H:1,6, and H:1,7) and a mutant flagellin obtained by site-directed mutagenesis of the fljB gene from serovar Typhimurium at codon 218, transforming threonine to alanine, expressed in Escherichia coli (fljB218(A)) were used to analyze the H1 antigenic complex. Cross-reactions were detected by Western blotting and dot blotting using commercial polyclonal antibodies against the different wild-type extracts and mutant FljB218(A). Therefore, we produced a monoclonal antibody (MAb), 23D4, isotyped as immunoglobulin M, against H:1,2 S. enterica serovar Typhimurium flagellin. The mutant flagellin was not recognized by this MAb. When a large number of phase 1 and phase 2 flagellin antigens of different serovars were used to characterize the 23D4 MAb, only extracts of serovars Typhimurium and [4,5,12:i:-] reacted. The protein composition of phase 1 and phase 2 extracts and highly purified H:1,2 flagellin from serovar Typhimurium strain LT2 and extract of strain 286 (serovar [4,5,12:i:-]), which reacted with the MAb, was studied. Phase 2 flagellin (FljB(H:1,2)) was detected in phase 1 and phase 2 flagellar heat extracts of serovar Typhimurium and was the single protein identified in all spots of purified H:1,2 flagellin. FliC, FlgK, and other proteins were detected in some immunoreactive spots and in the flagellar extract of serovar [4,5,12:i:-]. Immunoelectron microscopy of complete bacteria with 23D4 showed MAb attachment at the base of flagella, although the MAb failed to recognize the filament of flagella. Nevertheless, the results obtained by the other immunological tests (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Western blotting, and dot blotting) indicate a reaction against flagellins. The epitopes could also be shared by other proteins on spots where FljB is not present, such as aminopeptidase B, isocitrate lyase, InvE, EF-TuA, enolase, DnaK, and others. In conclusion, MAb 23D4 can be useful for detection and diagnostic purposes of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium and serovar [4,5,12:i:-] and could be also helpful for epitope characterization of flagellum-associated antigens.
Figures



References
-
- Aldridge, P., J. Karlinsey, and K. T. Hughes. 2003. The type III secretion chaperone FlgN regulates flagellar assembly via a negative feedback loop containing its chaperone substrates FlgK and FlgL. Mol. Microbiol. 49:1333-1345. - PubMed
-
- Barea, P. L., E. Calvo, J. A. Rodriguez, A. Rementeria, R. Calcedo, M. J. Sevilla, J. Ponton, and F. L. Hernando. 1999. Characterization of Candida albicans antigenic determinants by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and enhanced chemiluminescence. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 23:343-354. - PubMed
-
- Beutin, L., E. Strauch, S. Zimmermann, S. Kaulfuss, C. Schaudinn, A. Mannel, and H. R. Gelderblom. 2005. Genetical and functional investigation of fliC genes encoding flagellar serotype H4 in wild-type strains of Escherichia coli and in a laboratory E. coli K-12 strain expressing flagellar antigen type H48. BMC Microbiol. 5:4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell, A. M. 1991. Monoclonal antibody and immunosensor technology, p. 1-49. In P. C. van der Vliet (ed.), Laboratory techniques in biochemistry and molecular biology, vol. 23. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

