The use of a single-pill calcium channel blocker/statin combination in the management of hypertension and dyslipidemia: a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study
- PMID: 19125855
- PMCID: PMC8673228
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.00058.x
The use of a single-pill calcium channel blocker/statin combination in the management of hypertension and dyslipidemia: a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study
Abstract
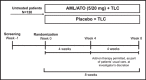
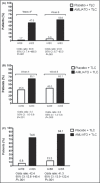
Poor control of hypertension or dyslipidemia may at least in part be due to these risk factors being treated in isolation. The Caduet in Untreated Subjects Population (CUSP) trial was an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy/safety of the combination of a calcium channel blocker (amlodipine besylate) and a statin (atorvastatin calcium) in a single-pill form (5/20 mg) plus therapeutic lifestyle changes (TLC) compared with placebo plus TLC in patients with comorbid hypertension and dyslipidemia without evidence of cardiovascular disease. At week 4, additional antihypertensive/lipid-lowering medication was permitted. The primary end point was the proportion of patients in whom the dual goal of blood pressure (<140/90 mm Hg) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol control (<100 mg/dL) was met at week 4. This dual goal attainment was significantly greater with amlodipine/atorvastatin plus TLC compared with placebo plus TLC at week 4 (47.6% vs 1.7%; P<.001), with further improvements at week 8. Most adverse events were mild to moderate. Therapy with single-pill amlodipine/atorvastatin plus TLC in these patients significantly increased dual blood pressure/low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal attainment compared with placebo plus TLC.
Figures
References
-
- Wong ND, Lopez VA, L’Italien G, et al. Inadequate control of hypertension in US adults with cardiovascular disease comorbidities in 2003–2004. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:2431–2436. - PubMed
-
- Hyre AD, Muntner P, Menke A, et al. Trends in ATP‐III‐defined high blood cholesterol prevalence, awareness, treatment and control among U.S. adults. Ann Epidemiol. 2007;17:548–555. - PubMed
-
- Johnson ML, Pietz K, Battleman DS, et al. Prevalence of comorbid hypertension and dyslipidemia and associated cardiovascular disease. Am J Manag Care. 2004;10:926–932. - PubMed
-
- Wong ND, Lopez V, Tang S, et al. Prevalence, treatment, and control of combined hypertension and hypercholesterolemia in the United States. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98:204–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

