Phase II trial of Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus expressing 5T4 and high dose Interleukin-2 (IL-2) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 19128501
- PMCID: PMC2631474
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-2
Phase II trial of Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus expressing 5T4 and high dose Interleukin-2 (IL-2) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-2 (IL-2) induces durable objective responses in a small cohort of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) but the antigen(s) responsible for tumor rejection are not known. 5T4 is a non-secreted membrane glycoprotein expressed on clear cell and papillary RCCs. A modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) encoding 5T4 was tested in combination with high-dose IL-2 to determine the safety, objective response rate and effect on humoral and cell-mediated immunity.
Methods: 25 patients with metastatic RCC who qualified for IL-2 were eligible and received three immunizations every three weeks followed by IL-2 (600,000 IU/kg) after the second and third vaccinations. Blood was collected for analysis of humoral, effector and regulatory T cell responses.
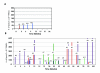
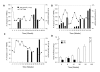
Results: There were no serious vaccine-related adverse events. While no objective responses were observed, three patients (12%) were rendered disease-free after nephrectomy or resection of residual metastatic disease. Twelve patients (48%) had stable disease which was associated with improved median overall survival compared to patients with progressive disease (not reached vs. 28 months, p = 0.0261). All patients developed 5T4-specific antibody responses and 13 patients had an increase in 5T4-specific T cell responses. Although the baseline frequency of Tregs was elevated in all patients, those with stable disease showed a trend toward increased effector CD8+ T cells and a decrease in Tregs.
Conclusion: Vaccination with MVA-5T4 did not improve objective response rates of IL-2 therapy but did result in stable disease associated with an increase in the ratio of 5T4-specific effector to regulatory T cells in selected patients.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN83977250.
Figures

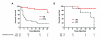
References
-
- Yang JC, Sherry RM, Steinberg SM, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, Hwu P, Seipp CA, Rogers-Freezer L, Morton KE, White DE, Liewehr DJ, Merino MJ, Rosenberg SA. Randomized Study of High-Dose and Low-Dose Interleukin-2 in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3127–3132. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.02.122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Schwartzentruber DJ, Hwu P, Marincola FM, Topalian SL, Restifo NP, Dudley ME, Schwarz SL, Spiess PJ, Wunderlich JR, Parkhurst MR, Kawakami Y, Seipp CA, Einhorn JH, White DE. Immunologic and therapeutic evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. Nat Med. 1998;4:321–327. doi: 10.1038/nm0398-321. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neumann E, Engelsberg A, Decker J, Storkel S, Jaeger E, Huber C, Seliger B. Heterogeneous Expression of the Tumor-associated Antigens RAGE-1, PRAME, and Glycoprotein 75 in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma: Candidates for T-Cell-based Immunotherapies? Cancer Res. 1998;58:4090–4095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

