Inhibition of PI3K increases oxaliplatin sensitivity in cholangiocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 19128511
- PMCID: PMC2628866
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-9-3
Inhibition of PI3K increases oxaliplatin sensitivity in cholangiocarcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Resistance of cholangiocarcinoma to chemotherapy is a major problem in cancer treatment. The mechanism of resistance is believed to involve phosphoinositide-3- kinase (PI3K)/Akt activation. Although the platinum-containing compound oxaliplatin has been extensively used in the treatment of several solid tumors, recent data regarding its use to treat cholangiocarcinoma are ambiguous. Oxaliplatin resistance in this disease could potentially involve PI3K pathways. We, therefore, examined the effects of PI3K pathways in cholangiocarcinoma cells in modulating oxaliplatin resistance.
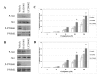
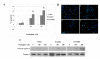
Results: After exposing the cholangiocarcinoma cell lines RMCCA1 and KKU100 to oxaliplatin, the levels of Akt and mTOR phosphorylation increased, as shown by western blot analysis. The WST-1 cell proliferation assay showed increased inhibition of cell growth under high concentrations of oxaliplatin. The combination of oxaliplatin with LY294002, an inhibitor of PI3K, resulted in a remarkable arrest of cell proliferation. Deactivation of mTOR by RAD001 was also synergistic with oxaliplatin, although to a lesser extent. The combination of oxaliplatin and a PI3K inhibitor also resulted in a significant induction of apoptosis, as demonstrated by the TUNEL assay.
Conclusion: Activation of PI3K might protect cholangiocarcinoma cells from oxaliplatininduced cytotoxicity. Although the inhibition of PI3K and the inhibition of mTOR both enhance oxaliplatin-induced cytotoxicity, PI3K inhibition has a greater effect. Targeting the PI3K pathway may be a useful approach to improve the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LY‑294002 enhances the chemosensitivity of liver cancer to oxaliplatin by blocking the PI3K/AKT/HIF‑1α pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jul;24(1):508. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12147. Epub 2021 May 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33982772 Free PMC article.
-
PKI-587 enhances chemosensitivity of oxaliplatin in hepatocellular carcinoma through suppressing DNA damage repair pathway (NHEJ and HR) and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Aug 15;11(8):5134-5149. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31497229 Free PMC article.
-
The mTOR inhibitor RAD001 sensitizes tumor cells to the cytotoxic effect of carboplatin in breast cancer in vitro.Anticancer Res. 2011 Sep;31(9):2713-22. Anticancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21868512
-
Combined targeting of AKT and mTOR using MK-2206 and RAD001 is synergistic in the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2013 Nov;133(9):2065-76. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28214. Epub 2013 May 29. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23588885
-
Overcoming acquired resistance to anticancer therapy: focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;71(4):829-42. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-2043-3. Epub 2013 Feb 3. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23377372 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic profiles of mesenchymal stem cells induced by a liver differentiation protocol.Int J Mol Sci. 2010;11(12):4905-15. doi: 10.3390/ijms11124905. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 21614181 Free PMC article.
-
Effective treatment of advanced colorectal cancer by rapamycin and 5-FU/oxaliplatin monitored by TIMP-1.J Gastrointest Surg. 2009 Oct;13(10):1781-90. doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-0948-x. Epub 2009 Jun 30. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009. PMID: 19565301
-
Expression of SLC22A18 regulates oxaliplatin resistance by modulating the ERK pathway in colorectal cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 15;12(3):1393-1408. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35411243 Free PMC article.
-
Increased activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is associated with cholangiocarcinoma metastasis and PI3K/mTOR inhibition presents a possible therapeutic strategy.Tumour Biol. 2013 Dec;34(6):3637-48. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0945-2. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23832540
-
Development of an In Vitro Assessment Method for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) by Integrating a Microphysiological System (MPS) with Morphological Deep Learning of Soma and Axonal Images.Toxics. 2023 Oct 10;11(10):848. doi: 10.3390/toxics11100848. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37888698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang W-L, Zhang X-C, Zhang D-W, Tong B-F. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of hepatic hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007;6:631–635. - PubMed
-
- Woynarowski JM, Faivre S, Herzig MC, Arnett B, Chapman WG, Trevino AV, Raymond E, Chaney SG, Vaisman A, Varchenko M, Juniewicz PE. Oxaliplatininduced damage of cellular DNA. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;58:920–927. - PubMed
-
- Androulakis N, Aravantinos G, Syrigos K, Polyzos A, Ziras N, Tselepatiotis E, Samonis G, Kentepozidis N, Giassas S, Vamvakas L, Georgoulias V. Oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in inoperable biliary tract carcinoma: a multicenter phase II study. Oncology. 2006;70:280–284. doi: 10.1159/000096249. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

