Phospholipid transfer protein Sec14 is required for trafficking from endosomes and regulates distinct trans-Golgi export pathways
- PMID: 19129178
- PMCID: PMC2652273
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808732200
Phospholipid transfer protein Sec14 is required for trafficking from endosomes and regulates distinct trans-Golgi export pathways
Abstract
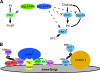
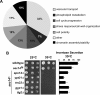
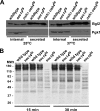
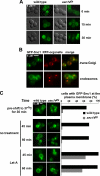
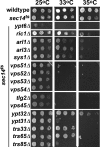
A protein known to regulate both lipid metabolism and vesicular transport is the phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylinositol transfer protein Sec14 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sec14 is thought to globally affect secretion from the trans-Golgi. The results from a synthetic genetic array screen for genes whose inactivation impaired growth of cells with a temperature-sensitive SEC14 allele implied Sec14 regulates transport into and out of the Golgi. This prompted us to examine the role of Sec14 in various vesicular transport pathways. We determined that Sec14 function was required for the route followed by Bgl2, whereas trafficking of other secreted proteins, including Hsp150, Cts1, Scw4, Scw10, Exg1, Cis3, and Ygp1, still occurred, indicating Sec14 regulates specific trans-Golgi export pathways. Upon diminution of Sec14 function, the v-SNARE Snc1 accumulated in endosomes and the trans-Golgi. Its accumulation in endosomes is consistent with Sec14 being required for transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi. Sec14 was also required for trafficking of Ste3 and the lipophilic dye FM4-64 from the plasma membrane to the vacuole at the level of the endosome. The combined genetic and cell biology data are consistent with regulation of endosome trafficking being a major role for Sec14. We further determined that lipid ligand occupancy differentially regulates Sec14 functions.
Figures



References
-
- Patton-Vogt, J. L., Griac, P., Sreenivas, A., Bruno, V., Dowd, S., Swede, M. J., and Henry, S. A. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272 20873-20883 - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Murray, J. P., and McMaster, C. R. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280 8544-8552 - PubMed
-
- Sreenivas, A., Patton-Vogt, J. L., Bruno, V., Griac, P., and Henry, S. A. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273 16635-16638 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

