Increased Nrf2 activation in livers from Keap1-knockdown mice increases expression of cytoprotective genes that detoxify electrophiles more than those that detoxify reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 19129213
- PMCID: PMC2644398
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfn267
Increased Nrf2 activation in livers from Keap1-knockdown mice increases expression of cytoprotective genes that detoxify electrophiles more than those that detoxify reactive oxygen species
Abstract
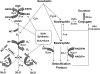
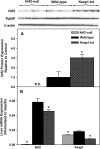
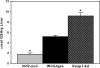
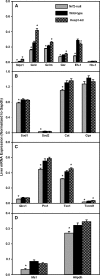
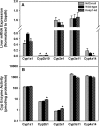
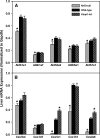
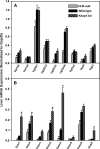
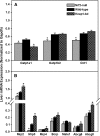
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a transcription factor critical for protection against electrophilic and oxidative stress. In a recently engineered mouse with knockdown of kelch-like ECH associated protein 1 (Keap1-kd mice), the cytosolic repressor of Nrf2, there is a 55% decrease in Keap1 mRNA and a 200% increase in Nrf2 protein in liver. Experiments with Nrf2-null mice have demonstrated the effects of a lack of Nrf2. However, little is known about the biological effects of more Nrf2 activation. Accordingly, the hepatic phenotype of Keap1-kd mice, as well as the hepatic mRNA expression of cytoprotective genes were compared among wild-type, Nrf2-null, and Keap1-kd mice. Three distinct patterns of hepatic gene expression were identified among wild-type, Nrf2-null, and Keap1-kd mice. The first pattern encompassed genes that were lower in Nrf2-null mice and considerably higher in Keap1-kd mice than wild-type mice, which included genes mainly responsible for the detoxification and elimination of electrophiles, such as NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 and glutathione-S-transferases (Gst), and multidrug resistance-associated proteins. The second pattern encompassed genes that were lower in Nrf2-null mice but not increased in Keap1-kd mice, and included genes, such as epoxide hydrolase-1, UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, aldehyde dehydrogenases, as well as genes important in the detoxification of reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide dismutase 1 and 2, catalase, and peroxiredoxin 1. The third pattern encompassed genes that were not different among wild-type, Nrf2-null, and Keap1-kd mice and included genes such as glutathione peroxidase, microsomal Gsts, and uptake transporters. In conclusion, the present study suggests that increased activation of hepatic Nrf2 is more important for the detoxification and elimination of electrophiles than reactive oxygen species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered disposition of acetaminophen in Nrf2-null and Keap1-knockdown mice.Toxicol Sci. 2009 May;109(1):31-40. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp047. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Toxicol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19246624 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 activation enhances biliary excretion of sulfobromophthalein by inducing glutathione-S-transferase activity.Toxicol Sci. 2009 May;109(1):24-30. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp045. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Toxicol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19246623 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of graded Nrf2 activation on phase-I and -II drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters in mouse liver.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e39006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039006. Epub 2012 Jul 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22808024 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 the rescue: effects of the antioxidative/electrophilic response on the liver.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 1;244(1):57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.01.013. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20122946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cytoprotective role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway.Arch Toxicol. 2011 Apr;85(4):241-72. doi: 10.1007/s00204-011-0674-5. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Arch Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21365312 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenovirus-Mediated Over-Expression of Nrf2 Within Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Protected Rats Against Acute Kidney Injury.Adv Pharm Bull. 2015 Jun;5(2):201-8. doi: 10.15171/apb.2015.028. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Adv Pharm Bull. 2015. PMID: 26236658 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced expression of Nrf2 in mice attenuates the fatty liver produced by a methionine- and choline-deficient diet.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15;245(3):326-34. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.03.016. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20350562 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ferroptosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Implications for Therapeutic Strategies.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 10;9(11):1660. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111660. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Introducing the "TCDD-inducible AhR-Nrf2 gene battery".Toxicol Sci. 2009 Oct;111(2):238-46. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp115. Epub 2009 May 27. Toxicol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19474220 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional response to oxidative stress during vertebrate development: effects of tert-butylhydroquinone and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 17;9(11):e113158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113158. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25402455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aleksunes LM, Manautou JE. Emerging role of Nrf2 in protecting against hepatic and gastrointestinal disease. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007;35:459–473. - PubMed
-
- Alnouti Y, Klaassen CD. Tissue distribution and ontogeny of sulfotransferase enzymes in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2006;93:242–255. - PubMed
-
- Ballatori N, Truong AT. Relation between biliary glutathione excretion and bile acid-independent bile flow. Am. J. Physiol. 1989;256:G22–G30. - PubMed
-
- Brangi M, Litman T, Ciotti M, Nishiyama K, Kohlhagen G, Takimoto C, Robey R, Pommier Y, Fojo T, Bates SE. Camptothecin resistance: Role of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC), mitoxantrone-resistance half-transporter (MXR), and potential for glucuronidation in MXR-expressing cells. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5938–5946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

