Age and comorbidities are effect modifiers of gender disparities in renal transplantation
- PMID: 19129311
- PMCID: PMC2653677
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008060591
Age and comorbidities are effect modifiers of gender disparities in renal transplantation
Abstract
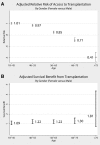
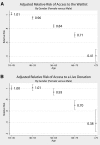
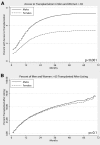
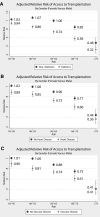
Women have less access to kidney transplantation than men, but the contributions of age and comorbidity to this disparity are largely unknown. We conducted a national cohort study of 563,197 patients with first-onset ESRD between 2000 and 2005. We used multivariate generalized linear models to evaluate both access to transplantation (ATT), defined as either registration for the deceased-donor waiting list or receiving a live-donor transplant, and survival benefit from transplantation, defined as the relative rate of survival after transplantation compared with the rate of survival on dialysis. We compared relative risks (RRs) between women and men, stratified by age categories and the presence of common comorbidities. Overall, women had 11% less ATT than men. When the model was stratified by age, 18- to 45-yr-old women had equivalent ATT to men (RR 1.01), but with increasing age, ATT for women declined dramatically, reaching a RR of 0.41 for those who were older than 75 yr, despite equivalent survival benefits from transplantation between men and women in all age subgroups. Furthermore, ATT for women with comorbidities was lower than that for men with the same comorbidities, again despite similar survival benefits from transplantation. This study suggests that there is no disparity in ATT for women in general but rather a marked disparity in ATT for older women and women with comorbidities. These disparities exist despite similar survival benefits from transplantation for men and women regardless of age or comorbidities.
Figures
References
-
- Cetingok M, Winsett RP, Hathaway DK: A comparative study of quality of life among the age groups of kidney transplant recipients. Prog Transplant 14: 33–38, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Humar A, Denny R, Matas AJ, Najarian JS: Graft and quality of life outcomes in older recipients of a kidney transplant. Exp Clin Transplant 1: 69–72, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Neipp M, Karavul B, Jackobs S, Meyer zu Vilsendorf A, Richter N, Becker T, Schwarz A, Klempnauer J: Quality of life in adult transplant recipients more than 15 years after kidney transplantation. Transplantation 81: 1640–1644, 2006 - PubMed
-
- White MJ, Ketefian S, Starr AJ, Voepel-Lewis T: Stress, coping, and quality of life in adult kidney transplant recipients. ANNA J 17: 421–424, 431, discussion 425, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Alexander GC, Sehgal AR: Barriers to cadaveric renal transplantation among blacks, women, and the poor. JAMA 280: 1148–1152, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

