Sensory input enhances synaptogenesis of adult-born neurons
- PMID: 19129387
- PMCID: PMC6664905
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4105-08.2009
Sensory input enhances synaptogenesis of adult-born neurons
Abstract
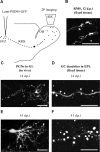
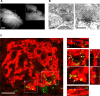
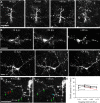
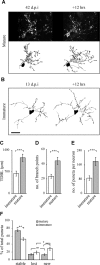
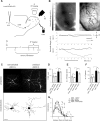
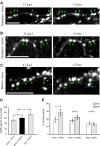
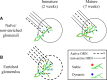
The adult mammalian brain maintains a prominent stem cell niche in the subventricular zone supplying new neurons to the olfactory bulb. We examined the dynamics of synaptogenesis by imaging the formation and elimination of clusters of a postsynaptic marker (PSD95), genetically targeted to adult-born neurons. We imaged in vivo adult-born periglomerular neurons (PGNs) during two phases of development, immaturity and maturity. Immature PGNs showed high levels of PSD95 puncta dynamics during 12-72 h intervals. Mature PGNs were more stable compared with immature PGNs but still remained dynamic, suggesting that synaptogenesis persists long after these neurons integrated into the network. By combining intrinsic signal and two photon imaging we followed PSD95 puncta in sensory enriched glomeruli. Sensory input upregulated the development of adult-born PGNs only in enriched glomeruli. Our data provide evidence for an activity-based mechanism that enhances synaptogenesis of adult-born PGNs during their initial phases of development.
Figures
References
-
- Altman J. Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis. 3. Dating the time of production and onset of differentiation of cerebellar microneurons in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1969;136:269–293. - PubMed
-
- Belenky MA, Smeraski CA, Provencio I, Sollars PJ, Pickard GE. Melanopsin retinal ganglion cells receive bipolar and amacrine cell synapses. J Comp Neurol. 2003;460:380–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
