Loss of modifier of cell adhesion reveals a pathway leading to axonal degeneration
- PMID: 19129390
- PMCID: PMC2669744
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3985-08.2009
Loss of modifier of cell adhesion reveals a pathway leading to axonal degeneration
Abstract
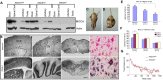
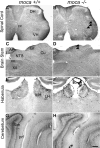
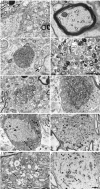
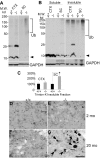
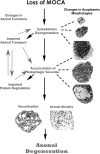
Axonal dysfunction is the major phenotypic change in many neurodegenerative diseases, but the processes underlying this impairment are not clear. Modifier of cell adhesion (MOCA) is a presenilin binding protein that functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rac1. The loss of MOCA in mice leads to axonal degeneration and causes sensorimotor impairments by decreasing cofilin phosphorylation and altering its upstream signaling partners LIM kinase and p21-activated kinase, an enzyme directly downstream of Rac1. The dystrophic axons found in MOCA-deficient mice are associated with abnormal aggregates of neurofilament protein, the disorganization of the axonal cytoskeleton, and the accumulation of autophagic vacuoles and polyubiquitinated proteins. Furthermore, MOCA deficiency causes an alteration in the actin cytoskeleton and the formation of cofilin-containing rod-like structures. The dystrophic axons show functional abnormalities, including impaired axonal transport. These findings demonstrate that MOCA is required for maintaining the functional integrity of axons and define a model for the steps leading to axonal degeneration.
Figures


References
-
- Arber S, Barbayannis FA, Hanser H, Schneider C, Stanyon CA, Bernard O, Caroni P. Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature. 1998;393:805–809. - PubMed
-
- Bray JJ, Fernyhough P, Bamburg JR, Bray D. Actin depolymerizing factor is a component of slow axonal transport. J Neurochem. 1992;58:2081–2087. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Sawchenko PE. Time course and distribution of inflammatory and neurodegenerative events suggest structural bases for the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Comp Neurol. 2007;502:236–260. - PubMed
-
- Cai D, Leem JY, Greenfield JP, Wang P, Kim BS, Wang R, Lopes KO, Kim SH, Zheng H, Greengard P, Sisodia SS, Thinakaran G, Xu H. Presenilin-1 regulates intracellular trafficking and cell surface delivery of β-amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:3446–3454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
