Artificial ligand binding within the HIF2alpha PAS-B domain of the HIF2 transcription factor
- PMID: 19129502
- PMCID: PMC2626723
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808092106
Artificial ligand binding within the HIF2alpha PAS-B domain of the HIF2 transcription factor
Abstract
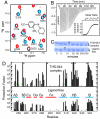
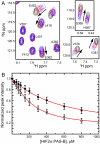
The hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) basic helix-loop-helix Per-aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT)-Sim (bHLH-PAS) transcription factors are master regulators of the conserved molecular mechanism by which metazoans sense and respond to reductions in local oxygen concentrations. In humans, HIF is critically important for the sustained growth and metastasis of solid tumors. Here, we describe crystal structures of the heterodimer formed by the C-terminal PAS domains from the HIF2alpha and ARNT subunits of the HIF2 transcription factor, both in the absence and presence of an artificial ligand. Unexpectedly, the HIF2alpha PAS-B domain contains a large internal cavity that accommodates ligands identified from a small-molecule screen. Binding one of these ligands to HIF2alpha PAS-B modulates the affinity of the HIF2alpha:ARNT PAS-B heterodimer in vitro. Given the essential role of PAS domains in forming active HIF heterodimers, these results suggest a presently uncharacterized ligand-mediated mechanism for regulating HIF2 activity in endogenous and clinical settings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
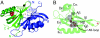

References
-
- Zagzag D, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in brain tumors: Association with angiogenesis, invasion, and progression. Cancer. 2000;88:2606–2618. - PubMed
-
- Bos R, et al. Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha independently predict prognosis in patients with lymph node negative breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;97:1573–1581. - PubMed
-
- Jiang BH, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R, Semenza GL. Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:17771–17778. - PubMed
-
- Zhulin IB, Taylor BL, Dixon R. PAS domain S-boxes in Archaea, Bacteria and sensors for oxygen and redox. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:331–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

