Limitations of structural allograft in revision total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 19130161
- PMCID: PMC2635432
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-008-0679-4
Limitations of structural allograft in revision total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
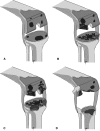
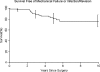
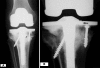
Management of large bone defects in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) usually has involved modular prostheses with metal augments, structural allografts, and megaprostheses. We retrospectively reviewed the outcome of treatment of major bone defects for 74 patients (79 knees) who had revision TKAs with structural allografts; nine patients were lost to followup before 5 years, leaving 65 patients (70 knees, or 88%) followed for a minimum of 5 years or until revision or death. Medical records, radiographs, patient surveys, and correspondence were used for all data. Sixteen patients (22.8%) had failed reconstructions and underwent additional revision surgery; eight of the 16 were secondary to allograft failure, three were secondary to failure of a component not supported by allograft, and five were secondary to infection. In patients not requiring revision surgery, the Knee Society score improved from 49 preoperatively to 87 postoperatively. We observed revision-free survival of 80.7% (95% confidence interval, 71.7-90.8) at 5 years and 75.9% (95% confidence interval, 65.6-87.8) at 10 years. Our data support the selective use of structural allograft for large cavitary defects encountered during TKA. However, the rates of complications and reoperations suggest efforts to improve results or develop more durable alternative methods are warranted for these challenging reconstructions.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures


References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/01.blo.0000214426.52206.2c', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000214426.52206.2c'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16672879', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16672879/'}]}
- Backstein D, Safir O, Gross A. Management of bone loss: structural grafts in revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;446:104–112. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11263645', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11263645/'}]}
- Clatworthy MG, Balance J, Brick GW, Chandler HP, Gross AE. The use of structural allograft for uncontained defects in revision total knee arthroplasty: a minimum five-year review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:404–411. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11570477', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11570477/'}]}
- Clatworthy MG, Gross AE. The allograft prosthetic composite: when and how. Orthopedics. 2001;24:897–898. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.arth.2004.03.002', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2004.03.002'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15190551', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15190551/'}]}
- Cuckler JM. Bone loss in total knee arthroplasty: graft augment and options. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19:56–58. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1054/arth.2002.32456', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1054/arth.2002.32456'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12068414', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12068414/'}]}
- Dennis DA. The structural allograft composite in revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:90–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

