Sample preparation module for bacterial lysis and isolation of DNA from human urine
- PMID: 19130239
- PMCID: PMC4442481
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-008-9277-1
Sample preparation module for bacterial lysis and isolation of DNA from human urine
Abstract
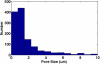
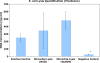
Silica impregnated polymer monolithic columns may provide a simple method for lysing and extracting DNA from bacteria inside of microfluidic chips. Here we use Escherichia coli as a test organism for a point of care thermoplastic microfluidic module designed to take in a urine sample, mix it with lysis buffer, and perform a hybrid chemical/mechanical lysis and solid phase extraction of nucleic acids from the sample. To demonstrate proof-of-concept, we doped human hematuric urine samples with E. coli at concentrations ranging from 10(1)-10(5) colony-forming units/mL (CFU/mL) to simulate patient samples. We then performed on-chip lysis and DNA extraction. The bacterial DNA was amplified using real-time PCR demonstrating lysis and isolation down to 10(1) CFU/mL. Results were comparable to a commercial kit at higher concentrations and performed better at recovering DNA at lower concentrations.
Figures


References
-
- Arroyo E, Wheeler EK, Shediac R, Hindson B, Nasarabadi S, Vrankovich G, Bell P, Bailey C, Sheppod T, Christian AT. Flow through pcr module of biobriefcase. Smart Medical and Biomedical Sensor Technology III, Proceedings of the SPIE, Vol. 6007. Proceedings of the SPIE. 2005
-
- Belgrader P, Hansford D, Kovacs GT, Venkateswaran K, Mariella Jr R, Milanovich F, Nasarabadi S, Okuzumi M, Pourahmadi F, Northrup MA. A minisonicator to rapidly disrupt bacterial spores for DNA analysis. Anal. Chem. 1999;71(19):4232–4236. doi:10.1021/ac990347o. - PubMed
-
- Bent S, Nallamothu BK, Simel DL, Fihn SD, Saint S. Does this woman have an acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection? JAMA. 2002;287(20):2701–2710. doi:10.1001/jama.287.20.2701. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya A, Klapperich CM. Thermoplastic microfluidic device for on-chip purification of nucleic acids for disposable diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2006;78(3):788–792. doi:10.1021/ac051449j. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

