Integrated microfluidic devices for combinatorial cell-based assays
- PMID: 19130244
- PMCID: PMC2893875
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-008-9260-x
Integrated microfluidic devices for combinatorial cell-based assays
Abstract
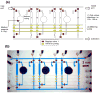
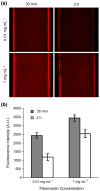
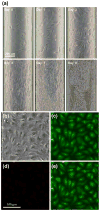
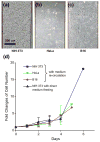
The development of miniaturized cell culture platforms for performing parallel cultures and combinatorial assays is important in cell biology from the single-cell level to the system level. In this paper we developed an integrated microfluidic cell-culture platform, Cell-microChip (Cell-microChip), for parallel analyses of the effects of microenvironmental cues (i.e., culture scaffolds) on different mammalian cells and their cellular responses to external stimuli. As a model study, we demonstrated the ability of culturing and assaying several mammalian cells, such as NIH 3T3 fibroblast, B16 melanoma and HeLa cell lines, in a parallel way. For functional assays, first we tested drug-induced apoptotic responses from different cell lines. As a second functional assay, we performed "on-chip" transfection of a reporter gene encoding an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) followed by live-cell imaging of transcriptional activation of cyclooxygenase 2 (Cox-2) expression. Collectively, our Cell-microChip approach demonstrated the capability to carry out parallel operations and the potential to further integrate advanced functions and applications in the broader space of combinatorial chemistry and biology.
Figures
References
-
- Chou HP, Unger MA, Quake SR. A microfabricated rotary pump. Biomed Microdevices. 2001;3(4):323–330. doi: 10.1023/ A:1012412916446. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

