The NAD World: a new systemic regulatory network for metabolism and aging--Sirt1, systemic NAD biosynthesis, and their importance
- PMID: 19130305
- PMCID: PMC2734380
- DOI: 10.1007/s12013-008-9041-4
The NAD World: a new systemic regulatory network for metabolism and aging--Sirt1, systemic NAD biosynthesis, and their importance
Abstract
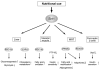
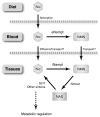
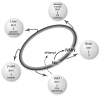
For the past several years, it has been demonstrated that the NAD-dependent protein deacetylase Sirt1 and nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt)-mediated systemic NAD biosynthesis together play a critical role in the regulation of metabolism and possibly aging in mammals. Based on our recent studies on these two critical components, we have developed a hypothesis of a novel systemic regulatory network, named "NAD World", for mammalian aging. Conceptually, in the NAD World, systemic NAD biosynthesis mediated by intra- and extracellular Nampt functions as a driver that keeps up the pace of metabolism in multiple tissues/organs, and the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 serves as a universal mediator that executes metabolic effects in a tissue-dependent manner in response to changes in systemic NAD biosynthesis. This new concept of the NAD World provides important insights into a systemic regulatory mechanism that fundamentally connects metabolism and aging and also conveys the ideas of functional hierarchy and frailty for the regulation of metabolic robustness and aging in mammals.
Figures
References
-
- Kenyon C. The plasticity of aging: insights from long-lived mutants. Cell. 2005;120:449–460. - PubMed
-
- Tatar M, Bartke A, Antebi A. The endocrine regulation of aging by insulin-like signals. Science. 2003;299:1346–1351. - PubMed
-
- Blander G, Guarente L. The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:417–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

