Intracellular calcium signals regulate growth of hepatic stellate cells via specific effects on cell cycle progression
- PMID: 19131107
- PMCID: PMC3018528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2008.11.006
Intracellular calcium signals regulate growth of hepatic stellate cells via specific effects on cell cycle progression
Abstract
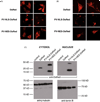
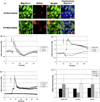
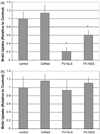
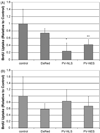
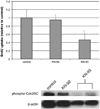
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are important mediators of liver fibrosis. Hormones linked to downstream intracellular Ca(2+) signals upregulate HSC proliferation, but the mechanisms by which this occurs are unknown. Nuclear and cytosolic Ca(2+) signals may have distinct effects on cell proliferation, so we expressed plasmid and adenoviral constructs containing the Ca(2+) chelator parvalbumin (PV) linked to either a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) or a nuclear export sequence (NES) to block Ca(2+) signals in distinct compartments within LX-2 immortalized human HSC and primary rat HSC. PV-NLS and PV-NES constructs each targeted to the appropriate intracellular compartment and blocked Ca(2+) signals only within that compartment. PV-NLS and PV-NES constructs inhibited HSC growth. Furthermore, blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca(2+) signals arrested growth at the G2/mitosis (G2/M) cell-cycle interface and prevented the onset of mitosis. Blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca(2+) signals downregulated phosphorylation of the G2/M checkpoint phosphatase Cdc25C. Inhibition of calmodulin kinase II (CaMK II) had identical effects on LX-2 growth and Cdc25C phosphorylation. We propose that nuclear and cytosolic Ca(2+) are critical signals that regulate HSC growth at the G2/M checkpoint via CaMK II-mediated regulation of Cdc25C phosphorylation. These data provide a new logical target for pharmacological therapy directed against progression of liver fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest that could inappropriately influence the work.
Figures




References
-
- Svegliati-Baroni G, Ridolfi F, Hannivoort R, Saccomanno S, Homan M, De Minicis S, Jansen PL, Candelaresi C, Benedetti A, Moshage H. Bile acids induce hepatic stellate cell proliferation via activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1042–1055. - PubMed
-
- Gabele E, Brenner DA, Rippe RA. Liver fibrosis: signals leading to the amplification of the fibrogenic hepatic stellate cell. Front Biosci. 2003;8:d69–d77. - PubMed
-
- Bataller R, Gines P, Nicolas JM, Gorbig MN, Garcia-Ramallo E, Gasull X, Bosch J, Arroyo V, Rodes J. Angiotensin II induces contraction and proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:1149–1156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

