A cis-acting diversification activator both necessary and sufficient for AID-mediated hypermutation
- PMID: 19132090
- PMCID: PMC2607555
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000332
A cis-acting diversification activator both necessary and sufficient for AID-mediated hypermutation
Abstract
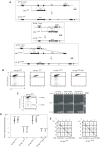
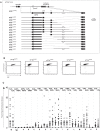
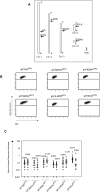
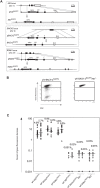
Hypermutation of the immunoglobulin (Ig) genes requires Activation Induced cytidine Deaminase (AID) and transcription, but it remains unclear why other transcribed genes of B cells do not mutate. We describe a reporter transgene crippled by hypermutation when inserted into or near the Ig light chain (IgL) locus of the DT40 B cell line yet stably expressed when inserted into other chromosomal positions. Step-wise deletions of the IgL locus revealed that a sequence extending for 9.8 kilobases downstream of the IgL transcription start site confers the hypermutation activity. This sequence, named DIVAC for diversification activator, efficiently activates hypermutation when inserted at non-Ig loci. The results significantly extend previously reported findings on AID-mediated gene diversification. They show by both deletion and insertion analyses that cis-acting sequences predispose neighboring transcription units to hypermutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Muramatsu M, Kinoshita K, Fagarasan S, Yamada S, Shinkai Y, et al. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell. 2000;102:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Arakawa H, Hauschild J, Buerstedde JM. Requirement of the activation-induced deaminase (AID) gene for immunoglobulin gene conversion. Science. 2002;295:1301–1306. - PubMed
-
- Harris RS, Sale JE, Petersen-Mahrt SK, Neuberger MS. AID is essential for immunoglobulin V gene conversion in a cultured B cell line. Curr Biol. 2002;12:435–438. - PubMed
-
- Di Noia J, Neuberger MS. Altering the pathway of immunoglobulin hypermutation by inhibiting uracil-DNA glycosylase. Nature. 2002;419:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Rada C, Di Noia JM, Neuberger MS. Mismatch recognition and uracil excision provide complementary paths to both Ig switching and the A/T-focused phase of somatic mutation. Mol Cell. 2004;16:163–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

