Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: the double-edged sword in apoptosis
- PMID: 19132226
- PMCID: PMC3674867
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: the double-edged sword in apoptosis
Abstract
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) is a multi-functional protein. It is a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activators; urokinase-plasminogen activator and tissue type plasminogen activator, and also plays an important role in regulating cell proliferation, adhesion, migration, and signal transduction pathways. These biological events are important processes during angiogenesis and restenosis. PAI-1 has been shown to regulate proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. The ability of PAI-1 to regulate cellular proliferation and migration has been attributed to its ability to control plasmin production, modify signaling pathways, and its inherent multifactorial ability to bind to vitronectin and lipoprotein receptor-related protein. However, the mechanism by which PAI-1 regulates the apoptotic pathway is not well understood. Evidence from the literature suggests that PAI-1 or its deficiency alters key signalling pathways, such as the PI3-k/Akt and the Jak/STAT pathways, and is involved in maintaining endothelial cell integrity thereby regulating cell death. Other investigators have demonstrated that PAI-1 directly binds to caspases as a mechanism of PAI-1-mediated cellular apoptosis. Moreover, results from studies assessing the role of PAI-1 in apoptosis have suggested that PAI-1 can exert pathogenic or protective effects, which may be related to the disease model or type of injury employed.
Figures
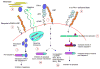
References
-
- Blasi F. uPA, uPAR, PAI-1: Key intersection of proteolytic, adhesive and chemotactic highways? Immunol Today. 1997;18:415–17. - PubMed
-
- Foekens JA, Peters H, Look M, et al. The urokinase system of plasminogen activation and prognosis in 2780 breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2000;60:636–43. - PubMed
-
- Devy L, Blacher S, Grignet-Debrus C, et al. The pro- or antiangiogenic effect of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 is dose dependent. FASEB J. 2002;16:147–54. - PubMed
-
- Bauriedel G, Hutter R, Welsch U, et al. Role of smooth muscle cell death in advanced coronary primary lesions: implications for plaque instability. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;41:480–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
