HPMA polymer-based site-specific delivery of oligonucleotides to hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 19133717
- PMCID: PMC2682209
- DOI: 10.1021/bc800237t
HPMA polymer-based site-specific delivery of oligonucleotides to hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
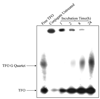
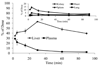
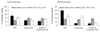
The objective was to determine whether bioconjugation of type I collagen specific triplex forming oligonucleotide (TFO) to N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide (HPMA) containing tetrapeptide Gly-Phe-Leu-Gly (GFLG) and mannose 6-phosphate (M6P) can provide their targeted delivery to hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Following bioconjugation, M6P-GFLG-HPMA-GFLG-32P-TFO was characterized by PAGE, HPLC, and GPC, and then its biodistribution was determined. TFO was dissociated from the conjugate when incubated with papain and formed triplex with the target DNA duplex. Type 1 collagen gene expression was significantly inhibited when HSC-T6 cells were transfected with this conjugate. Following tail vein injection into rats, M6P-GFLG-HPMA-GFLG-(32)P-TFO was rapidly cleared from the circulation and accumulated mainly in the liver. The plasma concentration versus time profile was biphasic, with 12.37 min as t(1/2) of distribution and 2886.48 min as t(1/2) of elimination. A large proportion of the injected M6P-GFLG-HPMA-GFLG-32P-TFO was taken up by the HSCs of both normal and fibrotic rats, which were isolated by liver perfusion at 30 min post-injection. Preinjection of M6P-GFLG-HPMA-GFLG-ONP into fibrotic rats decreased the liver uptake of the conjugates from 60% to 13%, suggesting M6P/TGFII receptor-mediated endocytosis of the conjugates by HSCs. Almost 80% of the total liver uptake in fibrotic rats was contributed by HSCs. In conclusion, conjugation with M6P-HPMA-GFLG significantly increased TFO delivery to the HSCs and could be potentially used for treating liver fibrosis.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Targeted TFO delivery to hepatic stellate cells.J Control Release. 2011 Oct 30;155(2):326-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.06.037. Epub 2011 Jul 8. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21763370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptor-mediated hepatic uptake of M6P-BSA-conjugated triplex-forming oligonucleotides in rats.Bioconjug Chem. 2006 May-Jun;17(3):823-30. doi: 10.1021/bc060006z. Bioconjug Chem. 2006. PMID: 16704223 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted delivery of a triplex-forming oligonucleotide to hepatic stellate cells.Biochemistry. 2005 Mar 22;44(11):4466-76. doi: 10.1021/bi047529j. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15766277
-
Biodistribution and hepatic uptake of triplex-forming oligonucleotides against type alpha1(I) collagen gene promoter in normal and fibrotic rats.Mol Pharm. 2005 May-Jun;2(3):206-17. doi: 10.1021/mp050012x. Mol Pharm. 2005. PMID: 15934781
-
Development of HPMA copolymer-anticancer conjugates: clinical experience and lessons learnt.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009 Nov 12;61(13):1131-48. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.05.007. Epub 2009 Aug 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009. PMID: 19699249 Review.
Cited by
-
Delivery and targeting of miRNAs for treating liver fibrosis.Pharm Res. 2015 Feb;32(2):341-61. doi: 10.1007/s11095-014-1497-x. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25186440 Review.
-
Ovarian Accumulation of Nanoemulsions: Impact of Mice Age and Particle Size.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 31;22(15):8283. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158283. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361049 Free PMC article.
-
Myofibroblast specific targeting approaches to improve fibrosis treatment.Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Dec 8;58(98):13556-13571. doi: 10.1039/d2cc04825f. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022. PMID: 36445310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted TFO delivery to hepatic stellate cells.J Control Release. 2011 Oct 30;155(2):326-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.06.037. Epub 2011 Jul 8. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21763370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunomodulatory function and antitumor effect of disulfiram: paving the way for novel cancer therapeutics.Discov Oncol. 2023 Jun 16;14(1):103. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00729-9. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37326784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

