Rickettsial outer-membrane protein B (rOmpB) mediates bacterial invasion through Ku70 in an actin, c-Cbl, clathrin and caveolin 2-dependent manner
- PMID: 19134120
- PMCID: PMC2773465
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01279.x
Rickettsial outer-membrane protein B (rOmpB) mediates bacterial invasion through Ku70 in an actin, c-Cbl, clathrin and caveolin 2-dependent manner
Abstract
Rickettsia conorii, an obligate intracellular tick-borne pathogen and the causative agent of Mediterranean spotted fever, binds to and invades non-phagocytic mammalian cells. Previous work identified Ku70 as a mammalian receptor involved in the invasion process and identified the rickettsial autotransporter protein, rOmpB, as a ligand; however, little is known about the role of Ku70-rOmpB interactions in the bacterial invasion process. Using an Escherichia coli heterologous expression system, we show here that rOmpB mediates attachment to mammalian cells and entry in a Ku70-dependent process. A purified recombinant peptide corresponding to the rOmpB passenger domain interacts with Ku70 and serves as a competitive inhibitor of adherence. We observe that rOmpB-mediated infection culminates in actin recruitment at the bacterial foci, and that this entry process relies in part on actin polymerization likely imparted through protein tyrosine kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent activities and microtubule stability. Small-interfering RNA studies targeting components of the endocytic pathway reveal that entry by rOmpB is dependent on c-Cbl, clathrin and caveolin-2. Together, these results illustrate that rOmpB is sufficient to mediate Ku70-dependent invasion of mammalian cells and that clathrin- and caveolin-dependent endocytic events likely contribute to the internalization process.
Figures


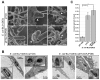
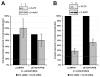
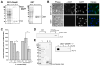
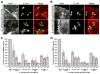
References
-
- Bandyopadhyay D, Mandal M, Adam L, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R. Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1568–1573. - PubMed
-
- Biswas D, Itoh K, Sasakawa C. Role of microfilaments and microtubules in the invasion of INT-407 cells by Campylobacter jejuni. Microbiology & Immunology. 2003;47:469–473. - PubMed
-
- Blanc G, Ngwamidiba M, Ogata H, Fournier PE, Claverie JM, Raoult D. Molecular Evolution of Rickettsia Surface Antigens: Evidence of Positive Selection. Mol Biol Evol 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

