Glucose-mediated tyrosine nitration in adipocytes: targets and consequences
- PMID: 19135148
- PMCID: PMC2888280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.12.010
Glucose-mediated tyrosine nitration in adipocytes: targets and consequences
Abstract
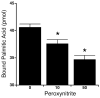
Hyperglycemia, a key factor in insulin resistance and diabetic pathology, is associated with cellular oxidative stress that promotes oxidative protein modifications. We report that protein nitration is responsive to changes in glucose concentrations in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Alterations in the extent of tyrosine nitration as well as the cellular nitroproteome profile correlated tightly with changing glucose concentrations. The target proteins we identified are involved in fatty acid binding, cell signaling, protein folding, energy metabolism, antioxidant capacity, and membrane permeability. The nitration of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (FABP4) at Tyr19 decreases, similar to phosphorylation, the binding of palmitic acid to the fatty acid-free protein. This potentially alters intracellular fatty acid transport, nuclear translocation of FABP4, and agonism of PPAR gamma. Our results suggest that protein tyrosine nitration may be a factor in obesity, insulin resistance, and the pathogenesis of diabetes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Glucose-modulated tyrosine nitration in beta cells: targets and consequences.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009 Apr 15;484(2):221-31. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2009.01.021. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2009. PMID: 19402213 Free PMC article.
-
LMO3 reprograms visceral adipocyte metabolism during obesity.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Aug;99(8):1151-1171. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02089-9. Epub 2021 May 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34018016 Free PMC article.
-
Vaspin promotes 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Nov;240(11):1520-7. doi: 10.1177/1535370214565081. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25585626 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-receptor tyrosine kinase and glucose transport.Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):565-75. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.565. Diabetes Care. 1990. PMID: 2162754 Review.
-
Tyrosine-Nitrated Proteins: Proteomic and Bioanalytical Aspects.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Mar 1;26(7):313-328. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6787. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27324931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric oxide blocks cellular heme insertion into a broad range of heme proteins.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Jun 1;48(11):1548-58. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.02.038. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20211245 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine Role of the Endothelium in Metabolic Homeostasis in Health and Nutrient Excess.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 26;9:882923. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.882923. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35557517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors influencing protein tyrosine nitration--structure-based predictive models.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Mar 15;50(6):749-62. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.12.016. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21172423 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Modifications as Manifestations of Hyperglycemic Glucotoxicity in Diabetes and Its Complications.Biochem Insights. 2016 Mar 23;9:1-9. doi: 10.4137/BCI.S36141. eCollection 2016. Biochem Insights. 2016. PMID: 27042090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the NO/superoxide ratio in adipose tissue: relevance to obesity and diabetes management.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;174(12):1570-1590. doi: 10.1111/bph.13498. Epub 2016 May 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27079449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muoio DM, Newgard CB. Mechanisms of disease: molecular and metabolic mechanisms of insulin resistance and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Cara JF, Chaiken RL. Type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2006;6:241–250. - PubMed
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Jones KL. Role of obesity in complicating and confusing the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes in children. Pediatrics. 2008;121:361–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

