Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and ultra-low dose cancer studies
- PMID: 19135172
- PMCID: PMC2895404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.12.002
Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and ultra-low dose cancer studies
Abstract
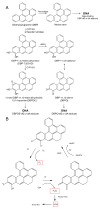
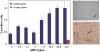
Cancer risk assessment utilizing rodents requires extrapolation across five orders of magnitude to estimate the Virtually Safe Dose (VSD). Regulatory agencies rely upon the Linear Extrapolated Dose (LED) except when sufficient information on mechanism of action justifies alternative models. Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) has been utilized at Oregon State University as a model for human cancer for forty years. Low cost and high capacity, made possible by our unique facility, along with low spontaneous background and high sensitivity, allow design and conduct of statistically challenging studies not possible in rodents. Utilization of custom microarrays demonstrates similarities in gene expression in trout and human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We have completed one study employing over 42,000 trout with dibenzo[a,l]pyrene (DBP) and determined the dose resulting in 1 additional cancer in 5000 animals, a 50-fold enhancement over the mouse ED(01) study. Liver tumor incidence at low dose deviated significantly from linearity (concave down), whereas, DBP-DNA adductions deviated slightly (convex up). A second study is underway with aflatoxin B(1) (AFB(1)). Results to date indicate AFB(1) at low dose, in contrast to DBP, elicits a linear dose-response function on the log-log scale which falls below the LED with a slope slightly greater than 1.0. Such studies demonstrate the statistical power of the trout cancer model and strengthen the case for incorporation of these data-sets into risk assessment for these environmental human carcinogens.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) tumor model: recent applications in low-dose exposures to tumor initiators and promoters.Toxicol Pathol. 2003 Jan-Feb;31 Suppl:58-61. Toxicol Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12597433 Review.
-
The rainbow trout liver cancer model: response to environmental chemicals and studies on promotion and chemoprevention.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;155(1):121-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2011.05.013. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21704190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of a rainbow trout oligonucleotide microarray to determine transcriptional patterns in aflatoxin B1-induced hepatocellular carcinoma compared to adjacent liver.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Dec;88(2):319-30. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi309. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16141433
-
Molecular dosimetry in fish: quantitative target organ DNA adduction and hepatocarcinogenicity for four aflatoxins by two exposure routes in rainbow trout.Mutat Res. 1998 Mar 20;399(2):233-44. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(97)00258-3. Mutat Res. 1998. PMID: 9672662
-
The importance of carcinogen dose in chemoprevention studies: quantitative interrelationships between, dibenzo[a,l]pyrene dose, chlorophyllin dose, target organ DNA adduct biomarkers and final tumor outcome.Carcinogenesis. 2007 Mar;28(3):611-24. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl174. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Carcinogenesis. 2007. PMID: 16973675
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Models Fit to ED001 Data on >40,000 Trout Exposed to Dibenzo[A,L]pyrene Indicate Mutations Do Not Drive Increased Tumor Risk.Dose Response. 2014 Jan 10;12(3):386-403. doi: 10.2203/dose-response.13-019.Bogen. eCollection 2014 Jul. Dose Response. 2014. PMID: 25249832 Free PMC article.
-
Effect on public health of a possible increase of the maximum level for 'aflatoxin total' from 4 to 10 μg/kg in peanuts and processed products thereof, intended for direct human consumption or use as an ingredient in foodstuffs.EFSA J. 2018 Feb 8;16(2):e05175. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5175. eCollection 2018 Feb. EFSA J. 2018. PMID: 32625810 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the CYP1A1 mRNA dose-response in human keratinocytes indicates that relative potencies of dioxins, furans, and PCBs are species and congener specific.Toxicol Sci. 2010 Dec;118(2):704-15. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq262. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Toxicol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20819910 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear cancer response at ultralow dose: a 40800-animal ED(001) tumor and biomarker study.Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 Jul;22(7):1264-76. doi: 10.1021/tx9000754. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19449824 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Mycotoxin Contamination of Aquaculture Feed: A Global Survey.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Mar 1;17(3):116. doi: 10.3390/toxins17030116. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alekseyev YO, Hamm ML, Essigmann JM. Aflatoxin B1 formamidopyrimidine adducts are preferentially repaired by the nucleotide excision repair pathway in vivo. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:1045–1051. - PubMed
-
- . Re-examination of the ED-01 study-risk assessment using time. Fund Appl Pharmacol. 1981a;1:88–123. - PubMed
-
- . Re-examination of the ED01 study. Review of statistics: the need for realistic statistical models for risk assessment. Fund Appl Pharmacol. 1981b;1:124–126. - PubMed
-
- Bailey GS, Dashwood R, Loveland PM, Pereira C, Hendricks JD. Molecular dosimetry in fish: quantitative target organ DNA adduction and hepatocarcinogenicity for four aflatoxins by two exposure routes in rainbow trout. Mut Res. 1997;339:233–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

