Regulation of PKD by the MAPK p38delta in insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 19135240
- PMCID: PMC2638021
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.018
Regulation of PKD by the MAPK p38delta in insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis
Abstract
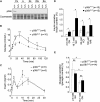
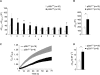
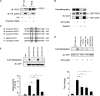
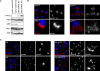
Dysfunction and loss of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells represent hallmarks of diabetes mellitus. Here, we show that mice lacking the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) p38delta display improved glucose tolerance due to enhanced insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. Deletion of p38delta results in pronounced activation of protein kinase D (PKD), the latter of which we have identified as a pivotal regulator of stimulated insulin exocytosis. p38delta catalyzes an inhibitory phosphorylation of PKD1, thereby attenuating stimulated insulin secretion. In addition, p38delta null mice are protected against high-fat-feeding-induced insulin resistance and oxidative stress-mediated beta cell failure. Inhibition of PKD1 reverses enhanced insulin secretion from p38delta-deficient islets and glucose tolerance in p38delta null mice as well as their susceptibility to oxidative stress. In conclusion, the p38delta-PKD pathway integrates regulation of the insulin secretory capacity and survival of pancreatic beta cells, pointing to a pivotal role for this pathway in the development of overt diabetes mellitus.
Figures
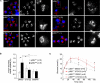

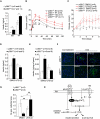
Comment in
-
p38delta and PKD1: kinase switches for insulin secretion.Cell. 2009 Jan 23;136(2):209-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.005. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19167323
References
-
- Adams R.H., Porras A., Alonso G., Jones M., Vintersten K., Panelli S., Valladares A., Perez L., Klein R., Nebreda A.R. Essential role of p38alpha MAP kinase in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:109–116. - PubMed
-
- Ammala C., Eliasson L., Bokvist K., Berggren P.O., Honkanen R.E., Sjoholm A., Rorsman P. Activation of protein kinases and inhibition of protein phosphatases play a central role in the regulation of exocytosis in mouse pancreatic beta cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1994;91:4343–4347. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Askari N., Diskin R., Avitzour M., Capone R., Livnah O., Engelberg D. Hyperactive variants of p38alpha induce, whereas hyperactive variants of p38gamma suppress, activating protein 1-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:91–99. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Mourney K., Proietto J., Morahan G., Andrikopoulos S. Too much of a good thing: why it is bad to stimulate the beta cell to secrete insulin. Diabetologia. 2008;51:540–545. - PubMed
-
- Bard F., Malhotra V. The formation of TGN-to-plasma-membrane transport carriers. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006;22:439–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

