The Escherichia coli cell division protein and model Tat substrate SufI (FtsP) localizes to the septal ring and has a multicopper oxidase-like structure
- PMID: 19135451
- PMCID: PMC2661564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.12.043
The Escherichia coli cell division protein and model Tat substrate SufI (FtsP) localizes to the septal ring and has a multicopper oxidase-like structure
Abstract
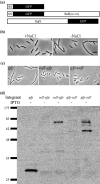
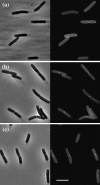
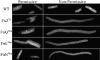
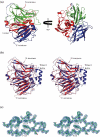
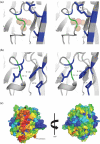
The Escherichia coli protein SufI (FtsP) has recently been proposed to be a component of the cell division apparatus. The SufI protein is also in widespread experimental use as a model substrate in studies of the Tat (twin arginine translocation) protein transport system. We have used SufI-GFP (green fluorescent protein) fusions to show that SufI localizes to the septal ring in the dividing cell. We have also determined the structure of SufI by X-ray crystallography to a resolution of 1.9 A. SufI is structurally related to the multicopper oxidase superfamily but lacks metal cofactors. The structure of SufI suggests it serves a scaffolding rather than an enzymatic role in the septal ring and reveals regions of the protein likely to be involved in the protein-protein interactions required to assemble SufI at the septal ring.
Figures

References
-
- Arends S.J.R., Williams K.B., Kustusch R.J., Weiss D.S., Erhmann M. The Periplasm. ASM Press; Washington, DC: 2007. Cell division; pp. 173–197.
-
- Goehring N.W., Beckwith J. Diverse paths to midcell: assembly of the bacterial cell division machinery. Curr. Biol. 2005;15:R514–R526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

