Influence of substituent modifications on the binding of 2-amino-1,8-naphthyridines to cytosine opposite an AP site in DNA duplexes: thermodynamic characterization
- PMID: 19136458
- PMCID: PMC2655693
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn1079
Influence of substituent modifications on the binding of 2-amino-1,8-naphthyridines to cytosine opposite an AP site in DNA duplexes: thermodynamic characterization
Abstract
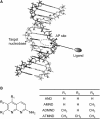
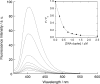
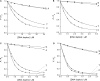
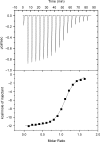
Here, we report on a significant effect of substitutions on the binding affinity of a series of 2-amino-1,8-naphthyridines, i.e., 2-amino-1,8-naphthyridine (AND), 2-amino-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridine (AMND), 2-amino-5,7-dimethyl-1,8-naphthyridine (ADMND) and 2-amino-5,6,7-trimethyl-1,8-naphthyridine (ATMND), all of which can bind to cytosine opposite an AP site in DNA duplexes. Fluorescence titration experiments show that the binding affinity for cytosine is effectively enhanced by the introduction of methyl groups to the naphthyridine ring, and the 1:1 binding constant (10(6) M(-1)) follows in the order of AND (0.30) < AMND (2.7) < ADMND (6.1) < ATMND (19) in solutions containing 110 mM Na(+) (pH 7.0, at 20 degrees C). The thermodynamic parameters obtained by isothermal titration calorimetry experiments indicate that the introduction of methyl groups effectively reduces the loss of binding entropy, which is indeed responsible for the increase in the binding affinity. The heat capacity change (DeltaC(p)), as determined from temperature dependence of the binding enthalpy, is found to be significantly different between AND (-161 cal/mol K) and ATMND (-217 cal/mol K). The hydrophobic contribution appears to be a key force to explain the observed effect of substitutions on the binding affinity when the observed binding free energy (DeltaG(obs)) is dissected into its component terms.
Figures



References
-
- Gottesfeld JM, Neely L, Trauger JW, Baird EE, Dervan PB. Regulation of gene expression by small molecules. Nature. 1997;387:202–205. - PubMed
-
- Dervan PB. Molecular recognition of DNA by small molecules. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001;9:2215–2235. - PubMed
-
- Spring DR. Chemical genetics to chemical genomics: small molecules offer big insghts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005;34:472–482. - PubMed
-
- Gewirtz DA. A critical evaluation of the mechanisms of action proposed for the antitumor effects of the anthracycline antibiotics adriamycin and daunorubicin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999;57:727–741. - PubMed

