The plastidial 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway provides the isoprenyl moiety for protein geranylgeranylation in tobacco BY-2 cells
- PMID: 19136647
- PMCID: PMC2648074
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.063248
The plastidial 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway provides the isoprenyl moiety for protein geranylgeranylation in tobacco BY-2 cells
Abstract
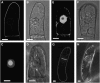
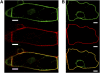
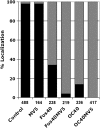
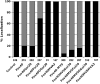
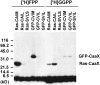
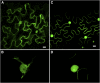
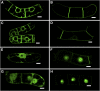
Protein farnesylation and geranylgeranylation are important posttranslational modifications in eukaryotic cells. We visualized in transformed Nicotiana tabacum Bright Yellow-2 (BY-2) cells the geranylgeranylation and plasma membrane localization of GFP-BD-CVIL, which consists of green fluorescent protein (GFP) fused to the C-terminal polybasic domain (BD) and CVIL isoprenylation motif from the Oryza sativa calmodulin, CaM61. Treatment with fosmidomycin (Fos) or oxoclomazone (OC), inhibitors of the plastidial 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway, caused mislocalization of the protein to the nucleus, whereas treatment with mevinolin, an inhibitor of the cytosolic mevalonate pathway, did not. The nuclear localization of GFP-BD-CVIL in the presence of MEP pathway inhibitors was completely reversed by all-trans-geranylgeraniol (GGol). Furthermore, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose (DX) reversed the effects of OC, but not Fos, consistent with the hypothesis that OC blocks 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthesis, whereas Fos inhibits its conversion to 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate. By contrast, GGol and DX did not rescue the nuclear mislocalization of GFP-BD-CVIL in the presence of a protein geranylgeranyltransferase type 1 inhibitor. Thus, the MEP pathway has an essential role in geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) biosynthesis and protein geranylgeranylation in BY-2 cells. GFP-BD-CVIL is a versatile tool for identifying pharmaceuticals and herbicides that interfere either with GGPP biosynthesis or with protein geranylgeranylation.
Figures

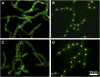
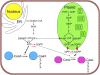
Comment in
-
A role for plastids in plant protein isoprenylation.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Mar;4(3):217-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.3.7842. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19721754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam, K.-P., Thiel, R., and Zapp, J. (1999). Incorporation of 1-[1-13C]deoxy-D-xylulose in chamomile sequiterpenes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 369 127–132. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama, T., and Chua, N.H. (1997). A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J. 11 605–612. - PubMed
-
- Bach, T.J. (1995). Some new aspects of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants - A review. Lipids 30 191–202. - PubMed
-
- Bach, T.J., and Lichtenthaler, H.K. (1983). Inhibition by mevinolin of plant growth, sterol formation and pigment accumulation. Physiol. Plant. 59 50–60.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

