Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells
- PMID: 19136945
- PMCID: PMC2674434
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07665
Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells
Erratum in
- Nature. 2009 Feb 26;457(7233):1168
Abstract
In an adaptive immune response, naive T cells proliferate during infection and generate long-lived memory cells that undergo secondary expansion after a repeat encounter with the same pathogen. Although natural killer (NK) cells have traditionally been classified as cells of the innate immune system, they share many similarities with cytotoxic T lymphocytes. We use a mouse model of cytomegalovirus infection to show that, like T cells, NK cells bearing the virus-specific Ly49H receptor proliferate 100-fold in the spleen and 1,000-fold in the liver after infection. After a contraction phase, Ly49H-positive NK cells reside in lymphoid and non-lymphoid organs for several months. These self-renewing 'memory' NK cells rapidly degranulate and produce cytokines on reactivation. Adoptive transfer of these NK cells into naive animals followed by viral challenge results in a robust secondary expansion and protective immunity. These findings reveal properties of NK cells that were previously attributed only to cells of the adaptive immune system.
Figures
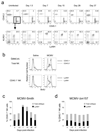
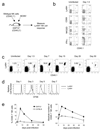
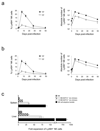

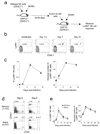

Comment in
-
Immunology: Natural killer cells remember.Nature. 2009 Jan 29;457(7229):544-5. doi: 10.1038/457544a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19177118 No abstract available.
-
A "memorable" NK cell discovery.Cell Res. 2009 Mar;19(3):277-8. doi: 10.1038/cr.2009.23. Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19252510 No abstract available.
References
-
- Harty JT, Badovinac VP. Shaping and reshaping CD8+ T-cell memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(2):107. - PubMed
-
- Kaech SM, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Effector and memory T-cell differentiation: implications for vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(4):251. - PubMed
-
- Sprent J, Surh CD. T cell memory. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:551. - PubMed
-
- Williams MA, Bevan MJ. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

