Genetic variation in PCDH11X is associated with susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19136949
- PMCID: PMC2873177
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.305
Genetic variation in PCDH11X is associated with susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
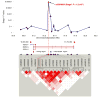
By analyzing late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) in a genome-wide association study (313,504 SNPs, three series, 844 cases and 1,255 controls) and evaluating the 25 SNPs with the most significant allelic association in four additional series (1,547 cases and 1,209 controls), we identified a SNP (rs5984894) on Xq21.3 in PCDH11X that is strongly associated with LOAD in individuals of European descent from the United States. Analysis of rs5984894 by multivariable logistic regression adjusted for sex gave global P values of 5.7 x 10(-5) in stage 1, 4.8 x 10(-6) in stage 2 and 3.9 x 10(-12) in the combined data. Odds ratios were 1.75 (95% CI = 1.42-2.16) for female homozygotes (P = 2.0 x 10(-7)) and 1.26 (95% CI = 1.05-1.51) for female heterozygotes (P = 0.01) compared to female noncarriers. For male hemizygotes (P = 0.07) compared to male noncarriers, the odds ratio was 1.18 (95% CI = 0.99-1.41).
Figures
References
-
- Evans DA, et al. Prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in a community population of older persons. Higher than previously reported. Jama. 1989;262:2551–6. - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921–3. - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, et al. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 1994;7:180–4. - PubMed
-
- Farrer LA, et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. Jama. 1997;278:1349–56. - PubMed
-
- Gatz M, et al. Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:168–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AG16574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG03949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AG020903/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG06576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG12716/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG25711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG18023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG21886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

