An RNA code for the FOX2 splicing regulator revealed by mapping RNA-protein interactions in stem cells
- PMID: 19136955
- PMCID: PMC2735254
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1545
An RNA code for the FOX2 splicing regulator revealed by mapping RNA-protein interactions in stem cells
Abstract
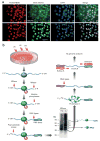
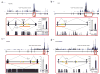
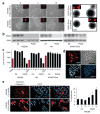
The elucidation of a code for regulated splicing has been a long-standing goal in understanding the control of post-transcriptional gene expression events that are crucial for cell survival, differentiation and development. We decoded functional RNA elements in vivo by constructing an RNA map for the cell type-specific splicing regulator FOX2 (also known as RBM9) via cross-linking immunoprecipitation coupled with high-throughput sequencing (CLIP-seq) in human embryonic stem cells. The map identified a large cohort of specific FOX2 targets, many of which are themselves splicing regulators, and comparison between the FOX2 binding profile and validated splicing events revealed a general rule for FOX2-regulated exon inclusion or skipping in a position-dependent manner. These findings suggest that FOX2 functions as a critical regulator of a splicing network, and we further show that FOX2 is important for the survival of human embryonic stem cells.
Figures
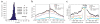

References
-
- Black DL. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:291–336. - PubMed
-
- Thomson JA, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Keller G. Embryonic stem cell differentiation: emergence of a new era in biology and medicine. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1129–1155. - PubMed
-
- Sonntag KC, Simantov R, Isacson O. Stem cells may reshape the prospect of Parkinson’s disease therapy. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;134:34–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

