High-resolution dynamic mapping of histone-DNA interactions in a nucleosome
- PMID: 19136959
- PMCID: PMC2635915
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1526
High-resolution dynamic mapping of histone-DNA interactions in a nucleosome
Abstract
The nature of the nucleosomal barrier that regulates access to the underlying DNA during many cellular processes is not fully understood. Here we present a detailed map of histone-DNA interactions along the DNA sequence to near base pair accuracy by mechanically unzipping single molecules of DNA, each containing a single nucleosome. This interaction map revealed a distinct approximately 5-bp periodicity that was enveloped by three broad regions of strong interactions, with the strongest occurring at the dyad and the other two about +/-40-bp from the dyad. Unzipping up to the dyad allowed recovery of a canonical nucleosome upon relaxation of the DNA, but unzipping beyond the dyad resulted in removal of the histone octamer from its initial DNA sequence. These findings have important implications for how RNA polymerase and other DNA-based enzymes may gain access to DNA associated with a nucleosome.
Figures

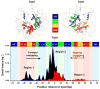


References
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–60. - PubMed
-
- Bondarenko VA, et al. Nucleosomes can form a polar barrier to transcript elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell. 2006;24:469–79. - PubMed
-
- Kireeva ML, et al. Nature of the nucleosomal barrier to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell. 2005;18:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Kireeva ML, et al. Nucleosome remodeling induced by RNA polymerase II: loss of the H2A/H2B dimer during transcription. Mol Cell. 2002;9:541–52. - PubMed
-
- Studitsky VM, Kassavetis GA, Geiduschek EP, Felsenfeld G. Mechanism of transcription through the nucleosome by eukaryotic RNA polymerase. Science. 1997;278:1960–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

