Formation of template-switching artifacts by linear amplification
- PMID: 19137105
- PMCID: PMC2563923
Formation of template-switching artifacts by linear amplification
Abstract
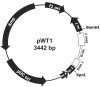
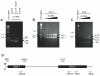
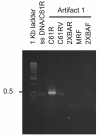
Linear amplification is a method of synthesizing single-stranded DNA from either a single-stranded DNA or one strand of a double-stranded DNA. In this protocol, molecules of a single primer DNA are extended by multiple rounds of DNA synthesis at high temperature using thermostable DNA polymerases. Although linear amplification generates the intended full-length single-stranded product, it is more efficient over single-stranded templates than double-stranded templates. We analyzed linear amplification over single- or double-stranded mouse H-ras DNA (exon 1-2 region). The single-stranded H-ras template yielded only the intended product. However, when the double-stranded template was used, additional artifact products were observed. Increasing the concentration of the double-stranded template produced relatively higher amounts of these artifact products. One of the artifact DNA bands could be mapped and analyzed by sequencing. It contained three template-switching products. These DNAs were formed by incomplete DNA strand extension over the template strand, followed by switching to the complementary strand at a specific Ade nucleotide within a putative hairpin sequence, from which DNA synthesis continued over the complementary strand.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Linear amplification mapping of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-reactive sequences in H-ras gene.DNA Cell Biol. 1998 Jun;17(6):529-39. doi: 10.1089/dna.1998.17.529. DNA Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9655246
-
Isolation of single-stranded DNA from loop-mediated isothermal amplification products.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Feb 1;290(4):1195-8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6334. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 11811989
-
Isothermal Amplification of Long, Discrete DNA Fragments Facilitated by Single-Stranded Binding Protein.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 17;7(1):8497. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09063-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28819114 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-nucleic acid interactions and DNA conformation in a complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase with a double-stranded DNA template-primer.Biopolymers. 1997;44(2):125-38. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1997)44:2<125::AID-BIP2>3.0.CO;2-X. Biopolymers. 1997. PMID: 9354757 Review.
-
Periodic assembly of nanospecies on repetitive DNA sequences generated on gold nanoparticles by rolling circle amplification.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;474:79-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-480-3_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 19031062 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplexed detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory infections in high throughput by SARSeq.Nat Commun. 2021 May 25;12(1):3132. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22664-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34035246 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-induced breaks are insufficient to break linkage drag surrounding the ToMV locus of Solanum lycopersicum.G3 (Bethesda). 2025 Jun 4;15(6):jkaf068. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf068. G3 (Bethesda). 2025. PMID: 40172925 Free PMC article.
-
Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) as a powerful novel alternative for differentiation of epizootic ISA virus variants.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037353. Epub 2012 May 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22624020 Free PMC article.
-
Two RNAs or DNAs May Artificially Fuse Together at a Short Homologous Sequence (SHS) during Reverse Transcription or Polymerase Chain Reactions, and Thus Reporting an SHS-Containing Chimeric RNA Requires Extra Caution.PLoS One. 2016 May 5;11(5):e0154855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154855. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27148738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakravarti D, Cavalieri EL, Rogan EG. Linear amplification mapping of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-reactive sequences in H-ras gene. DNA Cell Biol. 1998;17:529–539. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarti D, Mailander P, Franzen J, Higginbotham S, Cavalieri EL, Rogan EG. Detection of dibenzo[a,l]pyrene-induced H-ras codon 61 mutant genes in preneoplastic SENCAR mouse skin using a new PCR-RFLP method. Oncogene. 1998;16:3203–3210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
