Failure of artesunate-mefloquine combination therapy for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in southern Cambodia
- PMID: 19138388
- PMCID: PMC2628668
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-10
Failure of artesunate-mefloquine combination therapy for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in southern Cambodia
Abstract
Background: Resistance to anti-malarial drugs hampers control efforts and increases the risk of morbidity and mortality from malaria. The efficacy of standard therapies for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria was assessed in Chumkiri, Kampot Province, Cambodia.
Methods: One hundred fifty-one subjects with uncomplicated falciparum malaria received directly observed therapy with 12 mg/kg artesunate (over three days) and 25 mg/kg mefloquine, up to a maximum dose of 600 mg artesunate/1,000 mg mefloquine. One hundred nine subjects with uncomplicated vivax malaria received a total of 25 mg/kg chloroquine, up to a maximum dose of 1,500 mg, over three days. Subjects were followed for 42 days or until recurrent parasitaemia was observed. For P. falciparum infected subjects, PCR genotyping of msp1, msp2, and glurp was used to distinguish treatment failures from new infections. Treatment failure rates at days 28 and 42 were analyzed using both per protocol and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Real Time PCR was used to measure the copy number of the pfmdr1 gene and standard 48-hour isotopic hypoxanthine incorporation assays were used to measure IC50 for anti-malarial drugs.
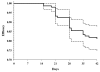
Results: Among P. falciparum infected subjects, 47.0% were still parasitemic on day 2 and 11.3% on day 3. The PCR corrected treatment failure rates determined by survival analysis at 28 and 42 days were 13.1% and 18.8%, respectively. Treatment failure was associated with increased pfmdr1 copy number, higher initial parasitaemia, higher mefloquine IC50, and longer time to parasite clearance. One P. falciparum isolate, from a treatment failure, had markedly elevated IC50 for both mefloquine (130 nM) and artesunate (6.7 nM). Among P. vivax infected subjects, 42.1% suffered recurrent P. vivax parasitaemia. None acquired new P. falciparum infection.
Conclusion: The results suggest that artesunate-mefloquine combination therapy is beginning to fail in southern Cambodia and that resistance is not confined to the provinces at the Thai-Cambodian border. It is unclear whether the treatment failures are due solely to mefloquine resistance or to artesunate resistance as well. The findings of delayed clearance times and elevated artesunate IC50 suggest that artesunate resistance may be emerging on a background of mefloquine resistance.
Figures

References
-
- Trape JF. The public health impact of chloroquine resistance in Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Zucker JR, Ruebush TK, Obonyo C, Otieno J, Campbell CC. The mortality consequences of the continued use of chloroquine in Africa: experience in Siaya, western Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68:386–390. - PubMed
-
- Vijaykadga S, Rojanawatsirivej C, Cholpol S, Phoungmanee D, Nakavej A, Wongsrichanalai C. In vivo sensitivity monitoring of mefloquine monotherapy and artesunate-mefloquine combinations for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Thailand in 2003. Trop Med Int Health. 2006;11:211–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2005.01557.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Denis MB, Tsuyuoka R, Poravuth Y, Narann TS, Seila S, Lim C, Incardona S, Lim P, Sem R, Socheat D, Christophel EM, Ringwald P. Surveillance of the efficacy of artesunate and mefloquine combination for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Cambodia. Trop Med Int Health. 2006;11:1360–1366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01690.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

